RMM system, a powerful tool for managing IT infrastructure, streamlines operations and enhances security across diverse environments. It offers a comprehensive suite of features that automate tasks, monitor performance, and ensure the smooth functioning of IT systems.
Table of Contents
From remote access and patch management to endpoint security and detailed reporting, RMM systems empower IT professionals to proactively address issues, mitigate risks, and optimize IT resources. Whether deployed in the cloud or on-premise, these solutions provide a centralized platform for managing and securing IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to focus on core operations and drive growth.
RMM System Overview
An RMM system, or Remote Monitoring and Management system, is a powerful tool for IT professionals seeking to streamline their operations and enhance the security of their client’s networks. These systems offer a comprehensive suite of functionalities that simplify tasks, automate processes, and provide real-time insights into the health and performance of IT infrastructure.
Key Functionalities
RMM systems are designed to provide a centralized platform for managing and monitoring IT environments remotely. They offer a wide range of features that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different organizations. Here are some of the core functionalities commonly found in RMM systems:
- Remote Access and Control: RMM systems allow technicians to access and control client devices remotely, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other administrative tasks without physically being on-site.
- Endpoint Security: RMM systems play a crucial role in bolstering endpoint security by providing real-time monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and automated patch management. They help identify and address security threats before they can exploit vulnerabilities.
- Network Monitoring: RMM systems continuously monitor network performance, identifying bottlenecks and potential issues. This allows IT professionals to proactively address problems and optimize network efficiency.
- Asset Management: RMM systems provide a comprehensive inventory of all devices and software within a network. This detailed information simplifies asset management tasks, such as software licensing and hardware tracking.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM systems generate insightful reports that provide valuable data on system performance, security threats, and user activity. This data helps IT professionals make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
- Automation and Scripting: RMM systems enable automation of repetitive tasks, such as software updates and system backups. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Benefits of Implementing an RMM Solution
Implementing an RMM system can bring significant benefits to organizations of all sizes. The key advantages include:
- Improved Security: RMM systems strengthen security posture by proactively identifying and mitigating threats, ensuring compliance with industry regulations, and automating security updates.
- Enhanced Productivity: RMM systems automate repetitive tasks, allowing IT staff to focus on more complex and strategic initiatives. This leads to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Reduced Costs: RMM systems can help reduce IT costs by minimizing downtime, optimizing resource utilization, and streamlining administrative processes.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By providing faster response times, proactive issue resolution, and enhanced security, RMM systems contribute to improved customer satisfaction.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RMM systems can easily scale to meet the evolving needs of organizations, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes.
Types of RMM Systems
RMM systems are available in various forms, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. The most common types include:
- Cloud-Based RMM: Cloud-based RMM systems are hosted on the provider’s servers, allowing users to access the platform from anywhere with an internet connection. They offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
- On-Premise RMM: On-premise RMM systems are installed and managed on the organization’s own servers. They offer greater control and customization but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
- Hybrid RMM: Hybrid RMM systems combine the benefits of cloud-based and on-premise solutions, offering flexibility and scalability while maintaining some level of control over the infrastructure.
RMM System Features
RMM systems offer a wide range of features designed to streamline IT management, improve security, and enhance overall efficiency. These features work together to provide a comprehensive solution for managing endpoints, networks, and applications across an organization.
Remote Access
Remote access capabilities are essential for IT professionals to connect to and manage devices remotely. This feature allows technicians to access endpoints, troubleshoot issues, and perform tasks without physically being present at the location.
- Secure Connection: RMM systems employ secure protocols like SSH and VPN to ensure that remote access sessions are encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
- Remote Control: Technicians can take control of remote devices, access their desktops, and perform actions as if they were physically present.
- File Transfer: Remote access features allow for the transfer of files between the technician’s workstation and the remote device, enabling software updates, configuration changes, and data transfer.
Patch Management
Patch management is crucial for maintaining the security and stability of endpoints. RMM systems automate the process of identifying, downloading, and installing software updates and security patches.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM systems continuously scan endpoints for vulnerabilities and outdated software.
- Automated Patching: Once patches are available, RMM systems can automatically download and install them on managed devices, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Patch Scheduling: IT professionals can schedule patch installations to minimize disruptions during peak business hours.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is a critical aspect of overall IT security. RMM systems offer various features to protect endpoints from malware, ransomware, and other threats.
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware: RMM systems often include built-in antivirus and anti-malware solutions to detect and remove threats.
- Firewall Management: RMM systems allow for the configuration and management of firewalls on endpoints, controlling network traffic and preventing unauthorized access.
- Data Loss Prevention: RMM systems can help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network by monitoring and controlling data transfers.
Reporting
RMM systems generate comprehensive reports that provide insights into the health, security, and performance of IT infrastructure.
- Asset Inventory: RMM systems can automatically inventory all devices and software on the network, providing a detailed overview of the IT environment.
- Security Reports: RMM systems generate reports on security vulnerabilities, malware detections, and other security-related events.
- Performance Monitoring: RMM systems track endpoint performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space, helping identify potential bottlenecks and performance issues.
RMM Vendor Feature Comparison
| Feature | Vendor A | Vendor B | Vendor C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Access | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Patch Management | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Endpoint Security | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Reporting | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mobile Device Management | Yes | No | Yes |
| Cloud Integration | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Pricing | Per device | Per agent | Per user |
RMM System Use Cases
RMM systems offer a wide range of applications across various industries, empowering businesses to manage their IT infrastructure effectively and efficiently. These systems provide comprehensive solutions for monitoring, managing, and automating tasks, ultimately improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Real-World Examples of RMM System Usage
RMM systems are utilized in diverse industries, including:
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics rely on RMM systems to ensure the smooth operation of their critical medical equipment, such as imaging systems, patient monitoring devices, and electronic health records (EHRs). These systems help maintain uptime, prevent data breaches, and comply with strict regulatory requirements.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions heavily depend on RMM systems to safeguard sensitive customer data and maintain compliance with industry regulations. RMM systems help monitor security threats, manage access controls, and ensure data integrity.
- Education: Educational institutions use RMM systems to manage their network infrastructure, desktops, and laptops used by students and staff. These systems facilitate remote access, software deployment, and security updates, ensuring a seamless learning experience.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies rely on RMM systems to manage their industrial control systems (ICS), automation equipment, and production lines. These systems help monitor performance, diagnose issues, and optimize production processes.
Scenarios Where RMM Systems Improve IT Operations
RMM systems can significantly enhance IT operations in various scenarios:
- Proactive Maintenance: RMM systems enable proactive maintenance by monitoring system performance, identifying potential issues before they escalate, and scheduling automated tasks for updates and repairs. This reduces downtime and minimizes disruptions.
- Remote Management: RMM systems allow IT professionals to manage and troubleshoot devices remotely, eliminating the need for on-site visits and reducing response times. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with geographically dispersed teams or remote offices.
- Security Monitoring and Management: RMM systems provide comprehensive security monitoring capabilities, including vulnerability scanning, malware detection, and endpoint protection. This helps organizations identify and mitigate security threats proactively.
- Software Deployment and Patch Management: RMM systems automate software deployment and patch management processes, ensuring that all devices are updated with the latest security patches and software versions. This reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and enhances overall security.
- Asset Management: RMM systems provide a centralized inventory of all devices, software, and licenses, enabling organizations to track their IT assets effectively. This facilitates efficient resource allocation and cost management.
Benefits of Using an RMM System
RMM systems offer numerous benefits, including:
| Use Case | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Proactive Maintenance | Reduced downtime, minimized disruptions, improved system stability |
| Remote Management | Increased efficiency, reduced response times, improved collaboration |
| Security Monitoring and Management | Enhanced security posture, reduced risk of breaches, improved compliance |
| Software Deployment and Patch Management | Improved security, reduced vulnerabilities, streamlined software updates |
| Asset Management | Efficient resource allocation, cost optimization, improved inventory control |
RMM System Security
RMM systems play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and enhancing overall IT security. They implement a range of security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure in RMM systems. It involves converting data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals. RMM solutions typically encrypt data at rest, meaning while stored on the system’s servers, and in transit, meaning during transmission between the RMM server and managed devices. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains protected.
Access Control
Access control is another critical security feature in RMM systems. It involves limiting user access to specific data and functions based on their roles and permissions. This helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive information or making changes to system configurations. RMM systems typically implement role-based access control (RBAC), where users are assigned roles with predefined permissions.
Scenario: Enhancing IT Security with RMM, Rmm system
Consider a scenario where a company uses an RMM system to manage its IT infrastructure. The RMM system automatically encrypts all sensitive data, including passwords, financial records, and customer information, both at rest and in transit. It also implements RBAC, assigning different roles to IT administrators, technicians, and end-users. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific data and functions.
Furthermore, the RMM system includes real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities. It detects suspicious activity, such as unauthorized login attempts or malware infections, and triggers alerts to the IT team. This allows the team to respond promptly and prevent potential security breaches.
RMM System Cost and ROI
Implementing an RMM system can significantly improve IT efficiency and security, but it’s essential to consider the costs and potential return on investment (ROI) before making a decision.
This section analyzes the cost factors associated with implementing an RMM system, explores the potential ROI from using such a solution, and compares the cost-effectiveness of different RMM vendors.
Cost Factors
The cost of implementing an RMM system can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the size of your organization, the complexity of your IT infrastructure, and the specific features you require.
Here are some of the key cost factors to consider:
- Software Subscription Fees: The cost of the RMM software subscription is typically based on the number of devices or endpoints you need to manage. Some vendors offer tiered pricing plans with different features and functionalities, while others charge a flat monthly fee per device.
- Hardware Costs: In some cases, you may need to invest in additional hardware, such as a server or network equipment, to support the RMM system. However, many RMM solutions are cloud-based, eliminating the need for significant hardware investments.
- Implementation and Training Costs: Implementing an RMM system can require time and resources, particularly if you have a complex IT environment. You may need to hire consultants or IT professionals to assist with the implementation process. Additionally, training your IT staff on how to use the RMM system can be a significant cost factor.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance Costs: Once the RMM system is implemented, you will need to factor in the ongoing costs of support and maintenance. This can include technical support, software updates, and security patches.
Potential ROI
While there are initial costs associated with implementing an RMM system, the potential ROI can be substantial. Here are some of the key benefits that can contribute to a positive ROI:
- Improved IT Efficiency: RMM systems automate many IT tasks, such as patch management, software updates, and system backups, freeing up your IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security: RMM systems provide comprehensive security features, including endpoint protection, vulnerability scanning, and threat detection, helping to reduce the risk of security breaches.
- Reduced Downtime: RMM systems can proactively identify and resolve issues before they cause downtime, reducing the impact on business operations.
- Improved Compliance: RMM systems can help organizations comply with industry regulations, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS, by automating compliance tasks and providing auditable records.
- Lower IT Costs: By automating tasks and reducing downtime, RMM systems can help organizations reduce their overall IT costs.
Cost-Effectiveness of Different RMM Vendors
The cost-effectiveness of different RMM vendors can vary significantly. Some vendors offer affordable pricing plans, while others charge a premium for their features and functionalities. When comparing vendors, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Pricing Plans: Compare the pricing plans of different vendors, considering the number of devices you need to manage, the features you require, and the length of the subscription term.
- Features and Functionality: Ensure that the vendor’s RMM solution offers the features and functionalities you need to meet your specific IT requirements.
- Customer Support: Look for a vendor that provides responsive and reliable customer support.
- Ease of Use: Choose a vendor whose RMM system is user-friendly and easy to learn and use.
- Integrations: Consider the vendor’s integration capabilities with other IT tools and systems.
RMM System Automation
RMM systems are designed to streamline IT operations by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up valuable time for IT professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automation is a key feature of RMM systems, allowing them to perform tasks like software updates and security checks without manual intervention.
Impact of Automation on IT Efficiency and Productivity
Automation can significantly improve IT efficiency and productivity. By automating repetitive tasks, IT teams can reduce the time and effort required to manage their systems, allowing them to focus on more complex issues and projects. This can lead to:
- Reduced workload: Automating tasks like software updates and security checks can significantly reduce the workload of IT staff, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improved response times: Automated tasks can be completed faster and more consistently than manual tasks, resulting in improved response times to user issues and faster resolution of problems.
- Increased accuracy: Automated tasks are less prone to human error, leading to increased accuracy and reliability of IT operations.
- Improved security: Automated security checks and updates can help to identify and mitigate security risks more effectively.
Examples of Specific Tasks That Can Be Automated
RMM systems can automate a wide range of tasks, including:
- Software updates: RMM systems can automatically download, install, and test software updates for all devices on the network. This ensures that all systems are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Security checks: RMM systems can automatically run security scans to identify vulnerabilities and malware infections. They can also automatically apply security patches and updates to mitigate identified risks.
- System monitoring: RMM systems can continuously monitor the health and performance of devices and applications. They can automatically alert IT staff to any issues that arise, allowing for proactive problem resolution.
- Backup and recovery: RMM systems can automatically back up critical data and systems, ensuring that data can be restored quickly and easily in the event of a disaster.
- Remote access: RMM systems can provide secure remote access to devices, allowing IT staff to troubleshoot and resolve issues without having to physically visit the device.
- Asset management: RMM systems can track and manage all hardware and software assets on the network, providing valuable insights into IT infrastructure and costs.
RMM System Reporting and Analytics
RMM systems are not just about managing endpoints; they are also powerful tools for gathering insights and making data-driven decisions. Reporting and analytics capabilities within RMM systems provide a comprehensive view of your IT infrastructure, enabling you to identify potential problems before they become critical, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall IT performance.
Reporting Capabilities
RMM systems offer a wide range of reporting capabilities, including:
- Dashboards: These provide a high-level overview of key metrics, such as device status, security vulnerabilities, and software updates. They allow for quick visualization of important information, making it easy to identify trends and potential issues.
- Alerts: RMM systems can generate alerts for various events, such as system failures, security breaches, and software update failures. These alerts can be customized based on your specific needs and can be delivered through various channels, such as email, SMS, or in-app notifications.
- Trend Analysis: RMM systems can analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns in your IT environment. This can help you understand the performance of your devices, the effectiveness of your security measures, and the impact of changes to your infrastructure.
Using RMM Reports for Proactive Issue Resolution
RMM reports can be instrumental in identifying and addressing IT issues proactively. By analyzing the data generated by the system, you can:
- Identify potential security vulnerabilities: Reports can highlight devices with outdated software, missing security patches, or weak passwords. This allows you to take timely action to mitigate risks and prevent breaches.
- Optimize resource allocation: RMM reports can reveal patterns in resource utilization, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. This information can help you optimize resource allocation and prevent performance bottlenecks.
- Predict and prevent system failures: By analyzing historical data, RMM systems can identify devices that are at risk of failure. This allows you to take preventative measures, such as replacing failing components or upgrading outdated hardware.
Sample Report
Imagine a report showing the number of devices with outdated antivirus software over the past three months. The report could display the following:
- Device count: The number of devices with outdated antivirus software for each month.
- Device types: The breakdown of devices by type (e.g., desktops, laptops, servers) with outdated antivirus software.
- Locations: The geographical location of devices with outdated antivirus software.
- Severity: The severity level of the vulnerability associated with outdated antivirus software.
This report would provide valuable insights into the organization’s security posture, allowing IT teams to prioritize patching efforts and mitigate potential risks.
RMM System Trends and Future Outlook
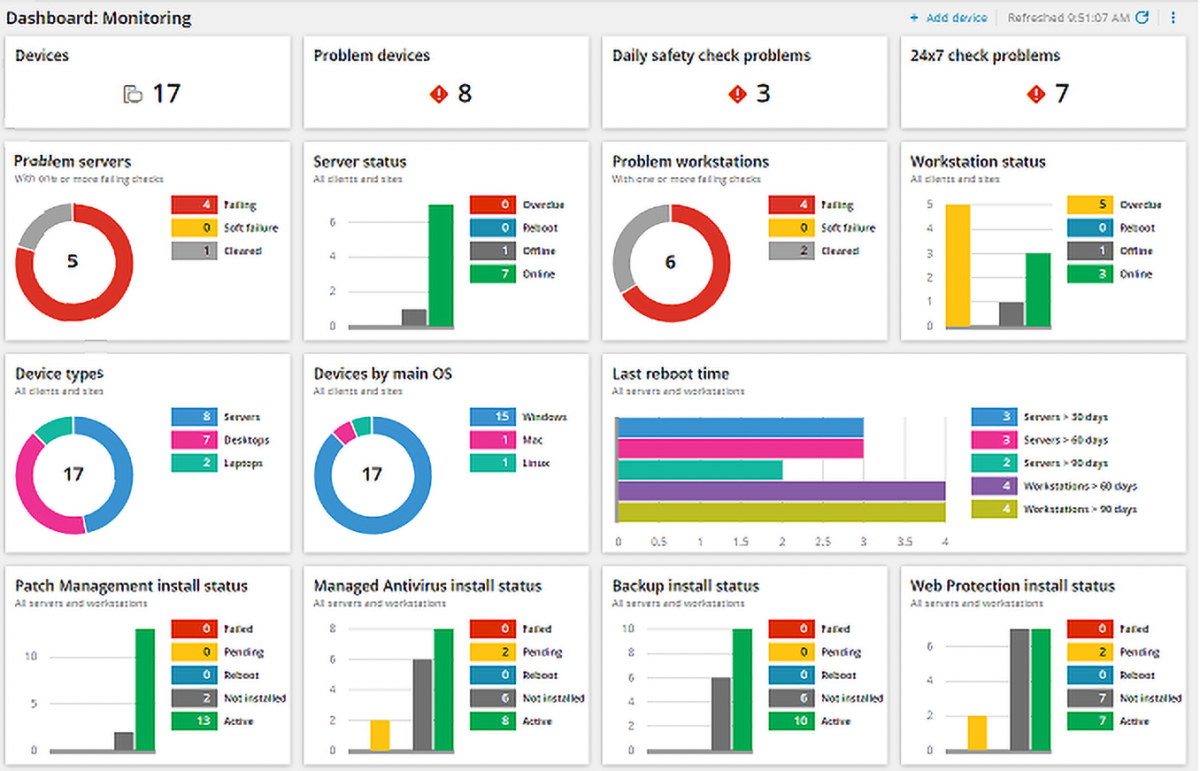
The RMM industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of IT environments. As businesses become more reliant on technology, the need for robust and efficient RMM solutions is growing.
Emerging Trends in the RMM Industry
The RMM industry is witnessing several emerging trends that are shaping the future of IT management. These trends are driven by the need for greater automation, improved security, and enhanced efficiency in managing IT infrastructure.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming the RMM landscape by automating tasks, providing predictive insights, and enhancing security. AI-powered RMM solutions can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential issues, predict failures, and optimize resource allocation. For example, AI can be used to detect anomalies in system behavior, predict hardware failures, and recommend proactive maintenance actions. This allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives and improve overall IT efficiency.
- Cloud Computing: The shift to cloud computing is driving the adoption of cloud-based RMM solutions. These solutions offer several benefits, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based RMM systems can manage devices and applications across different locations, enabling IT teams to remotely monitor and manage their entire IT infrastructure. For instance, cloud-based RMM solutions allow IT teams to deploy software updates, manage user accounts, and monitor security threats from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility and scalability make cloud-based RMM solutions an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
- Cybersecurity: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, RMM systems are playing a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity. RMM solutions can automate security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and endpoint protection. By integrating with security information and event management (SIEM) systems, RMM solutions can provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities. For example, RMM systems can automatically detect and quarantine infected devices, preventing the spread of malware within the network. This proactive approach to security helps businesses mitigate risks and protect their valuable data.
Future Potential of RMM Systems
RMM systems are poised to play an even more significant role in managing complex IT environments in the future. As businesses continue to adopt new technologies, the need for robust and scalable RMM solutions will only increase.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: RMM systems will integrate with emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing, and blockchain, to manage and secure connected devices and applications. This integration will enable IT teams to monitor and manage a wide range of devices and applications, from traditional desktops and laptops to smart devices and industrial equipment.
- Enhanced Automation and Proactive Management: RMM systems will continue to evolve towards greater automation, enabling IT teams to proactively manage IT infrastructure and prevent issues before they occur. AI-powered automation will automate routine tasks, freeing up IT professionals to focus on strategic initiatives and innovation. This proactive approach to IT management will reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and enhance overall IT performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: RMM systems will leverage data analytics to provide insights into IT performance and security posture. This data-driven approach will enable IT teams to make informed decisions about resource allocation, security investments, and future IT strategies. For example, RMM systems can analyze data on device usage, application performance, and security threats to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Evolving Landscape of RMM Solutions
The RMM landscape is constantly evolving, with new solutions and features emerging regularly.
- Specialized RMM Solutions: The RMM market is seeing the emergence of specialized solutions tailored to specific industries and use cases. For example, there are RMM solutions specifically designed for healthcare, education, and financial services, addressing the unique security and compliance requirements of these industries.
- Integration with Third-Party Tools: RMM solutions are increasingly integrating with third-party tools, such as ticketing systems, monitoring platforms, and security solutions. This integration allows IT teams to manage their IT infrastructure from a single platform, simplifying workflows and improving efficiency.
- Subscription-Based Models: RMM solutions are moving towards subscription-based models, offering flexible pricing options and access to the latest features and updates. This model provides businesses with predictable costs and ensures they have access to the most up-to-date technology.
Summary

In conclusion, RMM systems have become an indispensable asset for businesses seeking to optimize IT infrastructure, enhance security, and improve operational efficiency. By automating tasks, providing real-time insights, and streamlining workflows, RMM solutions empower IT teams to proactively manage and secure their systems, enabling them to focus on strategic initiatives and drive business growth.
An RMM system helps streamline IT tasks and manage endpoints efficiently. A key component of many RMM systems is the ability to handle media files, which can be crucial for businesses relying on video content. For instance, you might use Adobe Media Encoder to convert and optimize video files for various platforms, ensuring they are compatible with your RMM system’s distribution and management capabilities.
This integration helps maintain a consistent and efficient workflow for your IT infrastructure.


