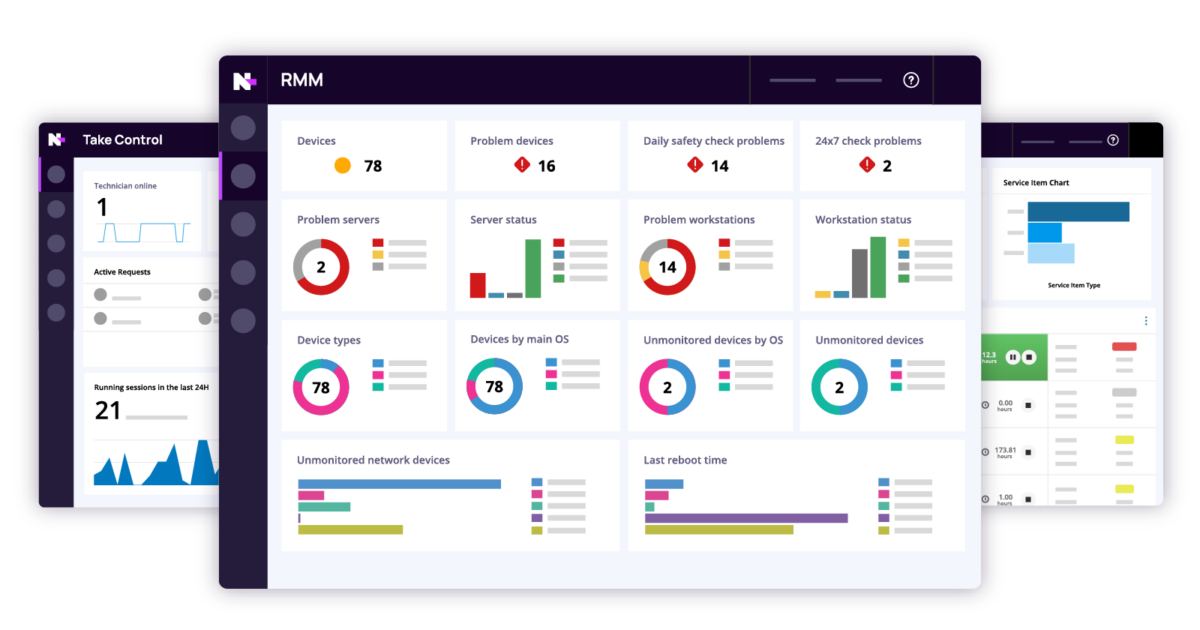
RMM Com, the acronym for Remote Monitoring and Management, encompasses a suite of software solutions designed to streamline and secure IT operations. Imagine having a watchful eye on your entire network, automatically detecting and resolving issues before they impact your business. This is the promise of RMM Com, empowering IT professionals and businesses to manage their infrastructure efficiently and effectively.
Table of Contents
RMM Com solutions offer a wide range of features, including patch management, endpoint security, remote access, and comprehensive reporting. These capabilities allow organizations to proactively address potential vulnerabilities, optimize performance, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Whether you’re a small business owner or a large enterprise, RMM Com provides the tools to simplify IT management and focus on your core business goals.
RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) Software Overview
RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) software is a powerful tool for IT professionals and businesses, allowing them to manage and monitor their IT infrastructure remotely. It provides a centralized platform for managing and securing endpoints, servers, and networks, streamlining IT operations and improving efficiency.
Key Functionalities of RMM Software
RMM software offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to simplify and enhance IT management. These functionalities include:
- Endpoint Management: RMM software enables centralized management of endpoints, including computers, laptops, and mobile devices. This includes tasks like software deployment, patch management, and configuration settings.
- Remote Access: Securely access and control remote devices, allowing for troubleshooting, software installation, and other administrative tasks without being physically present.
- Security Monitoring: Proactively monitor endpoints for security threats, including malware, vulnerabilities, and suspicious activity. RMM software can implement security policies, detect anomalies, and alert administrators to potential risks.
- Patch Management: Automate the process of patching operating systems, applications, and other software components, ensuring that devices are protected from known vulnerabilities.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate detailed reports on system performance, security events, and other relevant metrics. These insights help IT professionals identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall IT efficiency.
Benefits of Using RMM Software
RMM software offers numerous benefits for IT professionals and businesses, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks, such as software updates and security scans, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improved Security: Proactively monitor and manage security threats, reducing the risk of data breaches and system downtime.
- Reduced Costs: Streamline IT operations, minimize downtime, and optimize resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Productivity: Improve user experience by providing faster support and resolving issues more efficiently.
- Better Compliance: Ensure compliance with industry regulations and security standards by implementing and enforcing security policies.
RMM Software Use Cases
RMM software is a versatile tool that can be used across a wide range of industries and business sizes. Its ability to automate tasks, monitor systems, and provide remote access makes it a valuable asset for organizations of all shapes and sizes.
RMM Software Use Cases in Different Industries
RMM software can be applied in various industries, each with its own unique needs and challenges. Here are some examples:
- Healthcare: RMM software can be used to monitor medical equipment, ensuring its uptime and preventing downtime that could disrupt patient care. It can also be used to manage patient data securely, comply with HIPAA regulations, and provide remote support to healthcare professionals.
- Education: Schools and universities can use RMM software to manage student devices, provide remote access to educational resources, and ensure the security of sensitive student data. RMM can also help monitor network performance and troubleshoot connectivity issues, ensuring a smooth learning experience for students.
- Finance: Financial institutions rely heavily on RMM software to maintain the security and reliability of their systems. RMM can help monitor network traffic, detect security threats, and provide remote access for IT professionals to address issues quickly. It can also be used to manage compliance with regulations such as PCI DSS.
RMM Software Use Cases for Different Business Sizes
RMM software is suitable for businesses of all sizes, offering benefits tailored to their specific needs:
- Small Businesses: Small businesses often have limited IT resources and may not have the expertise to manage their systems effectively. RMM software can help them automate tasks, monitor their systems remotely, and receive alerts for potential problems. This allows them to focus on their core business while ensuring their IT infrastructure remains secure and operational.
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises have complex IT environments with numerous devices and users. RMM software can help them manage these environments effectively, automate tasks, and provide centralized control over their IT infrastructure. It can also help them improve security, comply with regulations, and reduce downtime.
RMM Software for On-Premise and Cloud-Based Environments
| Feature | On-Premise | Cloud-Based |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Installed and managed on-site | Hosted and managed in the cloud |
| Scalability | Can be challenging to scale | Highly scalable, able to accommodate growing needs |
| Security | Requires robust security measures to protect data | Leverages cloud provider security features |
| Cost | Initial investment may be higher, but ongoing costs can be lower | Lower initial investment, but ongoing costs may be higher |
| Maintenance | Requires on-site IT staff for maintenance and updates | Managed by the cloud provider, reducing maintenance burden |
Key Features of RMM Software
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software is a powerful tool that can help businesses of all sizes improve their IT operations. RMM software provides a comprehensive suite of features that can automate tasks, streamline workflows, and enhance security.
Essential Features of RMM Software
RMM software offers a range of features that can be categorized into core functionalities, which are essential for any organization using this technology.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM software allows IT professionals to remotely access and control devices, such as computers, servers, and mobile devices. This enables them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and manage configurations without being physically present at the location of the device.
- Patch Management: Keeping software up-to-date with the latest security patches is crucial to prevent vulnerabilities and attacks. RMM software automates the patch management process, ensuring that all devices are patched promptly and efficiently.
- Endpoint Security: RMM software plays a vital role in protecting endpoints from malware, ransomware, and other threats. It provides features like antivirus protection, firewall management, and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS).
- System Monitoring: RMM software monitors the health and performance of devices and systems, providing alerts and notifications in case of any issues. This helps IT teams proactively identify and resolve problems before they escalate.
- Asset Management: Tracking and managing IT assets, including hardware and software, is essential for efficient IT operations. RMM software provides features for asset inventory management, software licensing, and hardware lifecycle management.
Features for Different Types of Organizations
Different organizations have varying IT needs and requirements. RMM software offers features tailored to specific organizational needs.
- Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs): SMBs often prioritize affordability, ease of use, and comprehensive security. RMM software solutions for SMBs typically focus on core features like remote access, patch management, endpoint security, and basic monitoring.
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises often require more advanced features, including extensive reporting capabilities, integration with existing IT systems, and support for complex IT environments. RMM software solutions for enterprises offer features like multi-tenant management, advanced automation, and comprehensive compliance reporting.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs provide IT services to multiple clients and require robust RMM software solutions that can manage a large number of devices and clients efficiently. MSP-focused RMM software offers features like centralized management, automated billing and invoicing, and remote support tools.
Features of Popular RMM Software Solutions
Several popular RMM software solutions are available in the market, each with its own unique set of features. Here’s a table highlighting some of the key features of popular RMM software solutions:
| Feature | Datto RMM | Kaseya VSA | ConnectWise Manage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Access and Control | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Patch Management | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Endpoint Security | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| System Monitoring | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Asset Management | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Reporting and Analytics | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Automation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Integration | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mobile Device Management | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cloud Backup and Recovery | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Implementation and Integration of RMM Software

Successfully implementing and integrating RMM software requires a strategic approach that considers your organization’s unique IT environment and goals. The process involves careful planning, execution, and ongoing monitoring to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of the solution.
Steps Involved in Implementing RMM Software
Implementing RMM software involves a series of steps to ensure a successful transition and optimize its benefits.
- Needs Assessment: Begin by identifying your organization’s specific needs and objectives for RMM. This includes understanding the current IT infrastructure, security posture, and any pain points that RMM can address.
- Software Selection: Research and evaluate different RMM software solutions based on your requirements, budget, and technical capabilities. Consider factors like features, pricing, integrations, and customer support.
- Pilot Deployment: Before a full-scale rollout, conduct a pilot deployment on a limited set of devices or users to test the software’s functionality and identify any potential issues. This helps refine the implementation process and mitigate risks.
- Configuration and Customization: Configure the RMM software according to your organization’s specific needs and policies. This includes setting up alerts, defining security settings, and integrating with existing IT tools.
- User Training: Train IT staff and end-users on how to use the RMM software effectively. This ensures everyone understands its features and how to leverage its benefits.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor the RMM software’s performance and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal functionality and effectiveness. Regularly review reports and analytics to identify areas for improvement.
Best Practices for Integrating RMM Software, Rmm com
Successful integration of RMM software with existing IT infrastructure is crucial for seamless operation and data consistency.
- API Integration: Leverage APIs to connect the RMM software with other IT tools, such as ticketing systems, monitoring platforms, and security solutions. This enables data sharing and automation, streamlining workflows and improving efficiency.
- Data Synchronization: Ensure that data is synchronized between the RMM software and other systems to maintain consistency and avoid conflicts. This involves establishing data flow mechanisms and defining data mapping rules.
- Security Considerations: Implement robust security measures during integration, including access control, encryption, and data integrity checks. This protects sensitive information and ensures compliance with relevant regulations.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure it functions correctly and meets your requirements. This includes verifying data accuracy, API connectivity, and overall system stability.
Potential Challenges and Solutions During Implementation
Implementing RMM software can present challenges, but these can be addressed with careful planning and execution.
- Complexity of Integration: Integrating RMM software with complex IT environments can be challenging.
Solution: Break down the integration process into smaller, manageable tasks, and prioritize critical integrations first. Utilize skilled IT professionals with expertise in integration and automation.
- User Adoption: Encouraging user adoption of the new RMM software can be challenging.
Solution: Provide clear and concise training materials, offer ongoing support, and highlight the benefits of using the software. Address any user concerns promptly and provide tailored solutions.
- Data Migration: Migrating data from existing systems to the RMM software can be complex and time-consuming.
Solution: Plan the migration process carefully, develop data mapping rules, and test the migration process thoroughly. Consider using data migration tools to automate the process and reduce errors.
- Security Concerns: Implementing RMM software raises security concerns, especially regarding access control and data protection.
Solution: Implement robust security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits. Ensure compliance with relevant data protection regulations.
RMM Software Security Considerations: Rmm Com
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software provides valuable benefits for IT professionals, enabling them to manage and secure endpoints remotely. However, as with any powerful technology, RMM software also presents security risks that require careful consideration.
Security Risks Associated with RMM Software
RMM software introduces new attack vectors and vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. It’s essential to understand these risks to implement appropriate security measures.
- Unauthorized Access: If RMM software is not properly secured, attackers can gain unauthorized access to managed endpoints, potentially compromising sensitive data and systems.
- Data Breaches: RMM software stores and transmits sensitive information, such as credentials, network configurations, and system logs. If this data is intercepted or compromised, it can lead to significant data breaches.
- Malware Infection: RMM software can be a target for malware, which can then spread to managed endpoints, disrupting operations and compromising data security.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Attackers can target RMM software with DoS attacks, disrupting the ability of IT professionals to manage and monitor endpoints effectively.
- Insider Threats: Employees with access to RMM software could misuse their privileges, potentially leading to data breaches or system sabotage.
Best Practices for Securing RMM Software and Managed Endpoints
Protecting RMM software and managed endpoints requires a multi-layered approach that incorporates various security best practices.
- Strong Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to prevent unauthorized access to RMM software and managed endpoints. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, making it much harder for attackers to gain access.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep RMM software and managed endpoints up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Access Control: Implement robust access control policies to restrict access to RMM software and managed endpoints based on user roles and permissions. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate RMM software and managed endpoints from other sensitive networks to limit the impact of a security breach. Network segmentation helps prevent attackers from spreading laterally within the network.
- Security Monitoring and Logging: Implement comprehensive security monitoring and logging to detect suspicious activity and potential threats. This includes monitoring user activity, network traffic, and system logs.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data stored and transmitted by RMM software, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to attackers.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of security controls and identify potential vulnerabilities. This helps ensure that security measures are up-to-date and effective.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide security awareness training to employees to educate them about common security threats and best practices for protecting RMM software and managed endpoints. This helps reduce the risk of human error and insider threats.
Crucial Security Features for RMM Software Solutions
When selecting an RMM software solution, it’s crucial to consider the security features offered. Here are some essential features:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA is essential for preventing unauthorized access to RMM software. It adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC allows administrators to define granular permissions for different user roles, ensuring that users only have access to the information and resources they need to perform their tasks. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information stored and transmitted by RMM software. It ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to attackers.
- Security Auditing and Logging: Comprehensive security auditing and logging capabilities are crucial for detecting suspicious activity and potential threats. RMM software should provide detailed logs of user activity, network traffic, and system events.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Patch Management: RMM software should include vulnerability scanning and patch management capabilities to automatically identify and remediate vulnerabilities on managed endpoints. This helps ensure that systems are protected from known threats.
- Anti-Malware Protection: RMM software should offer integrated anti-malware protection to prevent malware infections on managed endpoints. This helps protect systems from malicious software that could compromise data security.
- Security Compliance Reporting: RMM software should provide security compliance reporting to help organizations demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations and standards. This can be essential for industries with strict data security requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
The Future of RMM Software
The landscape of remote monitoring and management (RMM) software is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing demands in the IT industry. As we look ahead, several emerging trends and innovative technologies are poised to shape the future of RMM solutions, offering businesses greater efficiency, security, and agility.
The Impact of AI and Automation on RMM Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming various aspects of IT management, and RMM software is no exception. AI-powered features are being integrated into RMM platforms to automate repetitive tasks, enhance security posture, and provide more insightful data analysis.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze historical data from endpoints to predict potential hardware failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. For instance, by analyzing patterns in system performance, an RMM solution can identify a hard drive nearing failure and alert administrators to replace it before it causes critical data loss.
- Automated Patch Management: AI-powered patch management systems can automatically identify and deploy security patches, ensuring that endpoints are always up-to-date and protected against vulnerabilities.
- Threat Detection and Response: AI can analyze network traffic and endpoint activity to detect and respond to threats in real-time, providing a more proactive and efficient approach to security.
Integration with Cloud and SaaS Platforms
The increasing adoption of cloud computing and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications is driving the need for RMM solutions that can seamlessly integrate with these platforms. This integration allows IT teams to manage and monitor both on-premises and cloud-based systems from a single pane of glass.
- Cloud-Based RMM Solutions: Many RMM vendors are offering cloud-based platforms that provide a scalable and flexible approach to managing IT infrastructure. This allows businesses to access RMM features from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for on-premises servers.
- Integration with SaaS Applications: RMM solutions are integrating with popular SaaS applications such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Zoom to provide a unified view of IT operations and streamline management tasks. This integration enables IT teams to monitor the performance and security of these applications alongside other endpoints.
Enhanced Security Features
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, RMM software is evolving to offer enhanced security features to protect businesses from attacks.
- Endpoint Security: RMM solutions are incorporating advanced endpoint security features such as next-generation antivirus (NGAV), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and behavioral analysis to detect and prevent malware infections.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): RMM platforms are integrating DLP capabilities to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network. This can include monitoring data transfers, identifying suspicious activity, and blocking unauthorized access to critical data.
- Zero-Trust Security: RMM solutions are adopting zero-trust security principles, which assume that no user or device can be trusted by default. This approach requires strict authentication and authorization measures to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data and resources.
The Rise of Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
The growth of managed service providers (MSPs) is driving the demand for robust and scalable RMM solutions. MSPs rely on RMM software to manage and monitor the IT infrastructure of their clients, offering a range of services such as remote support, security monitoring, and proactive maintenance.
- Automation and Efficiency: RMM software empowers MSPs to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and improve overall efficiency. This allows them to manage a larger number of clients with fewer resources.
- Centralized Management: RMM platforms provide MSPs with a centralized dashboard for managing multiple client environments, simplifying operations and improving visibility.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM solutions provide MSPs with comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing them to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
The Future of RMM: A Vision of Unified IT Management
In the future, RMM software is expected to become even more integrated and comprehensive, offering a unified platform for managing all aspects of IT infrastructure, including on-premises, cloud, and SaaS environments. This will enable businesses to simplify their IT operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
- Unified Dashboard: RMM solutions will provide a single dashboard for managing all IT assets, regardless of their location or type. This will allow IT teams to get a complete view of their IT infrastructure and proactively identify and address issues.
- AI-Driven Automation: AI and machine learning will continue to play a significant role in automating routine tasks, freeing up IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Predictive Analytics: RMM solutions will leverage predictive analytics to anticipate potential issues and proactively address them before they impact business operations.
RMM Software and Compliance
RMM software plays a crucial role in helping organizations meet compliance requirements. By automating tasks, streamlining processes, and providing comprehensive monitoring and reporting capabilities, RMM solutions enable businesses to effectively manage their IT infrastructure and ensure adherence to relevant regulations.
RMM Software and Compliance Requirements
RMM software helps organizations meet compliance requirements by providing a centralized platform for managing IT assets, security, and user access.
- Asset Management: RMM software helps organizations track and manage all their IT assets, including hardware, software, and network devices. This information is essential for meeting compliance requirements that mandate detailed asset inventories.
- Patch Management: RMM software automates the process of applying software updates and security patches to all devices in the network. This ensures that systems are always running the latest versions of software and are protected from known vulnerabilities, meeting compliance requirements related to vulnerability management.
- User Access Control: RMM software allows organizations to control user access to IT resources, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. This helps organizations comply with regulations that require strong access controls, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
- Security Monitoring: RMM software provides real-time monitoring of network activity and security events. This allows organizations to detect and respond to security threats quickly, reducing the risk of data breaches and meeting compliance requirements related to incident response and security monitoring.
- Reporting and Documentation: RMM software provides detailed reports and documentation on all aspects of IT infrastructure management. This documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance with regulations and for conducting audits.
RMM Software and Industry-Specific Regulations
RMM software is particularly valuable for organizations that need to comply with industry-specific regulations. Here’s how RMM software addresses some key regulations:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA regulations require healthcare organizations to protect patient health information (PHI). RMM software can help healthcare organizations meet HIPAA compliance by:
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit: RMM software can be used to encrypt all data stored on devices and to encrypt data transmissions between devices. This helps protect PHI from unauthorized access.
- Implementing strong access controls: RMM software allows organizations to control user access to PHI, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Auditing user activity: RMM software can be used to track user activity and to identify any suspicious activity. This helps organizations detect and investigate potential security breaches.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI DSS regulations require organizations that process credit card payments to protect cardholder data. RMM software can help organizations meet PCI DSS compliance by:
- Implementing strong password policies: RMM software can be used to enforce strong password policies for all users who have access to cardholder data. This helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Scanning for vulnerabilities: RMM software can be used to scan for vulnerabilities on all systems that handle cardholder data. This helps identify and fix security flaws that could be exploited by attackers.
- Monitoring network activity: RMM software can be used to monitor network activity for suspicious traffic that could indicate a security breach. This helps organizations detect and respond to attacks quickly.
RMM Software Features Supporting Compliance
RMM software includes various features specifically designed to support compliance efforts. These features include:
- Automated Patch Management: This feature ensures that all devices are patched regularly with the latest security updates, meeting compliance requirements related to vulnerability management.
- Vulnerability Scanning: This feature identifies security vulnerabilities on devices and networks, allowing organizations to address them proactively and meet compliance requirements related to vulnerability management.
- Security Auditing: This feature provides detailed reports on security events and user activity, helping organizations track compliance with regulations and conduct internal audits.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): This feature prevents sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network, meeting compliance requirements related to data protection.
- Endpoint Security: This feature provides real-time protection against malware and other threats, meeting compliance requirements related to endpoint security.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): This feature centralizes security logs from multiple sources, allowing organizations to analyze security events and identify potential threats, meeting compliance requirements related to security monitoring.
Closing Notes
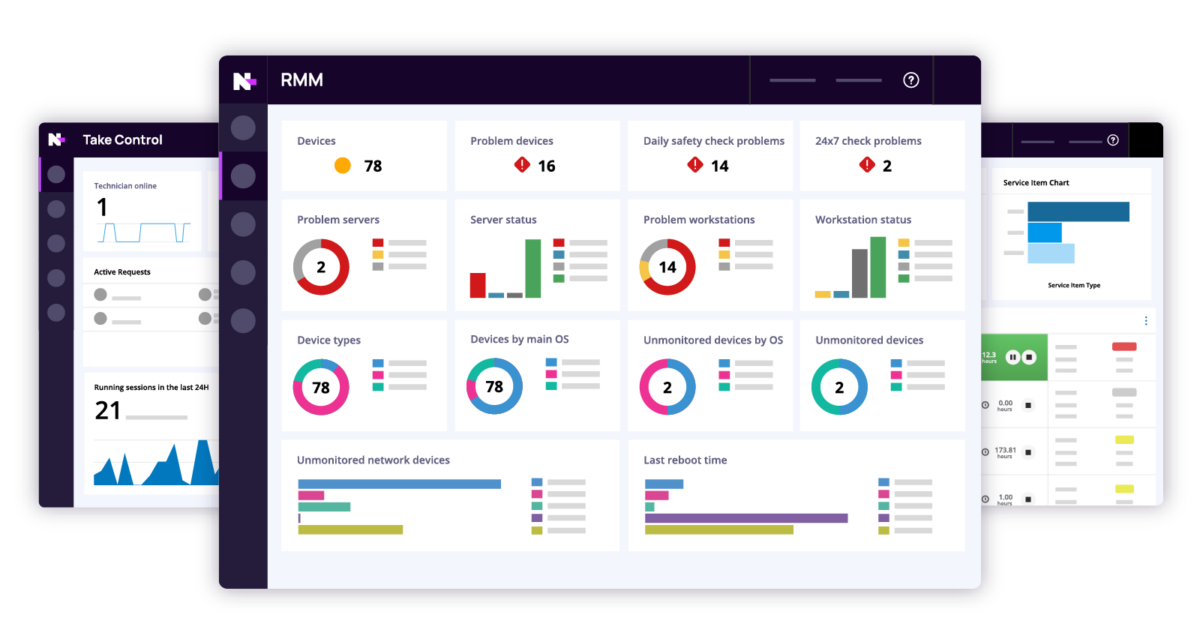
In conclusion, RMM Com has revolutionized the way IT is managed, empowering organizations to achieve greater efficiency, security, and compliance. From automating routine tasks to proactively addressing potential threats, RMM Com solutions offer a comprehensive approach to IT management. As technology continues to evolve, RMM Com is poised to play an even more critical role in shaping the future of IT operations.
RMM.com, a leading provider of remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions, focuses on streamlining IT operations for businesses of all sizes. Their platform leverages the synergy between hardware and software to ensure optimal performance and security across your entire IT infrastructure.
By understanding the intricacies of both hardware and software, RMM.com empowers businesses to proactively manage their IT systems, minimize downtime, and maximize productivity.