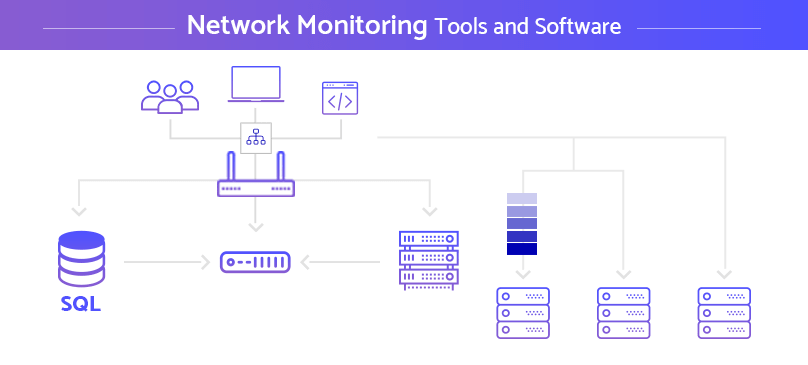
Remote network monitoring tools have become indispensable in today’s digital landscape, offering organizations a comprehensive view of their network infrastructure and enabling them to proactively address potential issues before they impact business operations.
Table of Contents
These tools empower IT professionals to monitor network performance, identify security threats, and optimize network resources, ensuring seamless connectivity and reliable data flow. From tracking bandwidth usage to detecting malicious activity, remote network monitoring tools play a critical role in maintaining network stability and resilience.
Introduction to Remote Network Monitoring Tools
Remote network monitoring refers to the practice of observing and analyzing network performance and activity from a location distant from the physical network infrastructure. It involves using specialized software and tools to collect data from various network devices, such as routers, switches, servers, and firewalls, and then presenting this information in a user-friendly format.
Remote network monitoring is essential in today’s digital landscape due to the increasing reliance on interconnected systems and the constant threat of cyberattacks. By providing real-time insights into network health, performance, and security, these tools enable organizations to proactively identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major disruptions.
Scenarios Where Remote Network Monitoring is Crucial
Remote network monitoring is crucial in a variety of scenarios, ensuring smooth operations and mitigating potential risks.
- Proactive Issue Detection and Resolution: Remote monitoring tools can detect anomalies and performance bottlenecks in real time, enabling prompt resolution before they impact users or services. For instance, if a network device is experiencing high CPU utilization or packet loss, the monitoring system can alert administrators, allowing them to investigate and resolve the issue before it causes network outages or performance degradation.
- Enhanced Security Posture: These tools can identify suspicious activities and potential security threats, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or denial-of-service attacks. By monitoring network traffic patterns, analyzing security logs, and detecting anomalies, administrators can quickly identify and mitigate security risks, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring network integrity.
- Improved Network Performance: Remote monitoring tools provide insights into network performance metrics, such as latency, bandwidth utilization, and packet loss. This data helps administrators identify performance bottlenecks, optimize network configurations, and ensure smooth operation of critical applications and services.
- Simplified Network Management: These tools centralize network management tasks, allowing administrators to monitor and manage multiple network devices and locations from a single console. This simplifies operations, reduces administrative overhead, and improves overall efficiency.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Remote monitoring systems can be instrumental in maintaining business continuity and disaster recovery plans. By providing real-time insights into network health and performance, these tools enable administrators to identify and respond to potential outages or disruptions, minimizing downtime and ensuring business operations continue uninterrupted.
Types of Remote Network Monitoring Tools
Remote network monitoring tools are essential for maintaining the health, security, and performance of modern networks. These tools provide valuable insights into network activity, enabling IT professionals to identify and resolve issues proactively.
Network Performance Monitoring Tools
Network performance monitoring tools are designed to track and analyze network performance metrics. These tools provide insights into network bandwidth utilization, latency, packet loss, and other key indicators. By monitoring these metrics, IT professionals can identify potential bottlenecks, optimize network resources, and ensure smooth network operation.
- Bandwidth Utilization Monitoring: These tools track the amount of network bandwidth being used at different times, helping to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize network resource allocation.
- Latency Monitoring: Latency monitoring tools track the time it takes for data packets to travel between different points on the network. This helps to identify slowdowns and performance issues, particularly for time-sensitive applications.
- Packet Loss Monitoring: These tools track the percentage of data packets that are lost during transmission. Packet loss can be caused by various factors, such as network congestion or hardware failures, and can significantly impact network performance.
- Network Traffic Analysis: Network performance monitoring tools can analyze network traffic patterns, identifying trends and anomalies that may indicate performance issues. This helps IT professionals to proactively address potential problems before they impact users.
Security Monitoring Tools
Security monitoring tools are crucial for detecting and preventing security threats. These tools monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, analyze log files for potential security breaches, and provide real-time alerts when threats are detected.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These tools analyze network traffic for known attack signatures and alert administrators when suspicious activity is detected. IDS can help to prevent unauthorized access to network resources and mitigate the impact of security breaches.
- Firewall Management: Security monitoring tools often include features for managing firewalls, allowing administrators to configure firewall rules, monitor firewall activity, and respond to security incidents.
- Vulnerability Scanning: These tools scan network devices and applications for known security vulnerabilities, helping to identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Log Analysis: Security monitoring tools often include log analysis capabilities, allowing administrators to analyze security logs for suspicious activity, identify patterns of malicious behavior, and track security incidents over time.
Application Performance Monitoring Tools
Application performance monitoring tools focus on tracking the performance of specific applications running on the network. These tools provide insights into application response times, error rates, and resource utilization, helping to identify and resolve performance bottlenecks.
- Response Time Monitoring: These tools track the time it takes for applications to respond to user requests, helping to identify slowdowns and performance issues.
- Error Rate Monitoring: Application performance monitoring tools track the frequency of application errors, helping to identify potential problems and ensure application stability.
- Resource Utilization Monitoring: These tools track the amount of CPU, memory, and other resources being used by applications, helping to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize application performance.
- User Experience Monitoring: Some application performance monitoring tools include features for tracking user experience, such as website loading times and application responsiveness, providing insights into how users are experiencing applications.
Log Management Tools
Log management tools are essential for collecting, storing, and analyzing log data from various network devices and applications. These tools provide a centralized repository for log data, making it easier to identify and troubleshoot issues, investigate security incidents, and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Log Collection: Log management tools collect log data from various sources, including network devices, servers, and applications, providing a comprehensive view of network activity.
- Log Storage: These tools provide secure and reliable storage for log data, ensuring that it is readily available for analysis and auditing purposes.
- Log Analysis: Log management tools offer powerful analysis capabilities, allowing administrators to search, filter, and correlate log data to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Alerting and Reporting: Log management tools can generate alerts when suspicious activity is detected in log data and provide reports on network activity and security incidents.
Network Traffic Analysis Tools
Network traffic analysis tools provide deep insights into network traffic patterns, allowing IT professionals to understand how the network is being used, identify potential security threats, and optimize network performance.
- Protocol Analysis: Network traffic analysis tools can analyze network traffic at the protocol level, providing detailed information about the types of traffic flowing through the network.
- Traffic Flow Analysis: These tools can track the flow of traffic between different network devices, identifying patterns of communication and potential bottlenecks.
- Packet Capture and Analysis: Network traffic analysis tools can capture and analyze individual network packets, providing detailed information about the content and structure of network traffic.
- Security Threat Detection: Network traffic analysis tools can be used to identify suspicious traffic patterns, such as malware communication or denial-of-service attacks.
| Type of Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Network Performance Monitoring Tools | – Provides comprehensive insights into network performance. – Enables proactive identification and resolution of performance issues. – Helps optimize network resource allocation. |
– Can be complex to configure and manage. – May require significant investment in hardware and software. – Can generate large amounts of data that require careful analysis. |
| Security Monitoring Tools | – Detects and prevents security threats. – Provides real-time alerts when threats are detected. – Helps to ensure network security and compliance. |
– Can generate a high volume of alerts, requiring careful analysis and prioritization. – May require specialized expertise to configure and manage. – Can be expensive to implement and maintain. |
| Application Performance Monitoring Tools | – Provides insights into application performance and user experience. – Helps identify and resolve performance bottlenecks. – Improves application stability and reliability. |
– Can be complex to configure and integrate with applications. – May require significant investment in hardware and software. – Can generate large amounts of data that require careful analysis. |
| Log Management Tools | – Provides a centralized repository for log data. – Enables comprehensive analysis of network activity. – Helps to troubleshoot issues, investigate security incidents, and comply with regulations. |
– Can be complex to configure and manage. – May require significant storage capacity. – Can generate a large volume of data that requires careful analysis. |
| Network Traffic Analysis Tools | – Provides deep insights into network traffic patterns. – Enables identification of potential security threats. – Helps optimize network performance. |
– Can be complex to configure and manage. – May require specialized expertise to interpret data. – Can generate large amounts of data that require careful analysis. |
Benefits of Using Remote Network Monitoring Tools
Remote network monitoring tools provide organizations with a comprehensive and insightful view of their network infrastructure, enabling them to identify potential issues, optimize performance, and enhance security. These tools offer a wide range of benefits, contributing to improved network efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced security posture.
Enhanced Network Security
Remote network monitoring tools play a crucial role in strengthening network security by providing real-time visibility into network traffic and identifying suspicious activities. These tools can detect anomalies, potential threats, and security breaches, allowing organizations to respond quickly and effectively.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Remote network monitoring tools can detect and prevent unauthorized access to network resources. By analyzing network traffic patterns, these tools can identify suspicious activities, such as brute-force attacks, malware infections, and data exfiltration attempts. Real-time alerts and automated responses can help organizations mitigate security threats proactively.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Remote network monitoring tools can scan for vulnerabilities in network devices, applications, and operating systems. This allows organizations to identify and patch security flaws before they can be exploited by attackers. Regular vulnerability assessments ensure that networks are protected against known threats and vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Monitoring: Organizations in regulated industries must comply with specific security standards and regulations. Remote network monitoring tools can help organizations track compliance with these regulations by providing real-time visibility into network activities and ensuring that security policies are enforced. This includes monitoring access controls, data encryption, and other security measures.
Improved Network Performance
Remote network monitoring tools enable organizations to gain insights into network performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimize network efficiency. By analyzing network metrics and identifying performance issues, organizations can proactively address problems before they impact users or applications.
- Performance Monitoring: Remote network monitoring tools provide real-time data on network performance, including bandwidth utilization, latency, and packet loss. This data can be used to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize network configurations for optimal performance.
- Troubleshooting and Optimization: When performance issues arise, remote network monitoring tools can help identify the root cause of the problem. By analyzing network traffic and performance metrics, organizations can quickly diagnose and resolve network issues, minimizing downtime and improving user experience.
- Capacity Planning: Remote network monitoring tools can help organizations predict future network requirements and plan for capacity expansion. By analyzing historical network data, organizations can identify trends and anticipate future needs, ensuring that the network infrastructure can support growing business demands.
Reduced Downtime
Downtime can be costly for organizations, disrupting business operations and impacting productivity. Remote network monitoring tools can help minimize downtime by providing early warning signs of potential issues and enabling proactive problem resolution.
- Proactive Issue Detection: Remote network monitoring tools can detect potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By monitoring network metrics, these tools can identify early warning signs of network instability, device failures, or other issues that could lead to downtime. This allows organizations to take corrective action before the issue impacts users or applications.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: Remote network monitoring tools can send automated alerts and notifications to IT personnel when network issues are detected. This ensures that problems are addressed promptly, minimizing the impact on network performance and reducing downtime.
- Remote Access and Management: Remote network monitoring tools provide IT personnel with remote access to network devices and applications. This allows them to diagnose and resolve issues remotely, minimizing the need for on-site visits and reducing downtime.
Proactive Issue Detection and Resolution
Remote network monitoring tools empower organizations to proactively identify and resolve network issues before they impact users or applications. This proactive approach reduces downtime, improves network performance, and enhances overall network stability.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Remote network monitoring tools provide real-time data on network performance, security, and device status. This allows organizations to identify potential issues as they arise and take corrective action before they escalate into major problems.
- Automated Incident Response: Remote network monitoring tools can automate incident response procedures, reducing the time it takes to resolve issues. When a problem is detected, these tools can trigger predefined actions, such as sending alerts, isolating affected devices, or launching automated troubleshooting scripts.
- Historical Data Analysis: Remote network monitoring tools capture and store historical network data. This data can be analyzed to identify trends, predict future issues, and improve network performance over time. By understanding historical patterns, organizations can optimize network configurations and prevent recurring problems.
Increased Network Visibility
Remote network monitoring tools provide organizations with a comprehensive view of their network infrastructure, enabling them to gain insights into network performance, security, and device status. This increased visibility helps organizations make informed decisions about network management and security.
- Centralized Dashboard: Remote network monitoring tools provide a centralized dashboard that displays real-time data on network performance, security, and device status. This dashboard gives IT personnel a comprehensive view of the network, allowing them to quickly identify and address issues.
- Detailed Reports and Analytics: Remote network monitoring tools generate detailed reports and analytics that provide insights into network performance, security trends, and user behavior. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement, optimize network configurations, and enhance security measures.
- Network Mapping and Topology: Remote network monitoring tools can create network maps and topologies that visualize the physical and logical layout of the network. This helps IT personnel understand the relationships between devices and applications, facilitating troubleshooting and network management.
Choosing the Right Remote Network Monitoring Tool
Selecting the ideal remote network monitoring tool is crucial for ensuring optimal network performance, security, and uptime. The right tool can help you identify and resolve issues proactively, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Remote Network Monitoring Tool
The process of selecting a remote network monitoring tool involves careful consideration of various factors that align with your specific needs and circumstances.
- Network Size and Complexity
- Budget Constraints
- Specific Monitoring Requirements
- Integration Capabilities
- Ease of Use
Network Size and Complexity
The size and complexity of your network are fundamental factors influencing your tool selection.
- Small networks with limited devices and simple configurations may benefit from basic, affordable tools with fewer features.
- Large, complex networks with numerous devices, diverse protocols, and geographically dispersed locations require comprehensive, feature-rich tools with advanced capabilities for managing and monitoring diverse network elements.
Budget Constraints
Budget limitations are a critical consideration in tool selection.
- Open-source tools offer a cost-effective solution, particularly for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
- Commercial tools provide comprehensive features and support, but they come with a price tag, which may be more suitable for larger enterprises with greater financial resources.
Specific Monitoring Requirements, Remote network monitoring tools
Understanding your specific monitoring needs is essential.
- Identify the specific network elements you need to monitor, such as servers, routers, switches, firewalls, and applications.
- Determine the types of metrics you need to track, including performance, security, availability, and resource utilization.
Integration Capabilities
Seamless integration with existing systems is crucial for efficient monitoring.
- Ensure the tool integrates with your existing infrastructure, such as your ticketing system, security information and event management (SIEM) platform, or other monitoring tools.
- Integration capabilities streamline workflows, reduce manual intervention, and provide a unified view of your network health.
Ease of Use
The tool should be user-friendly, regardless of your technical expertise.
- Choose a tool with a clear interface, intuitive navigation, and comprehensive documentation to simplify monitoring tasks.
- Consider the availability of training resources and support options to ensure a smooth learning curve.
Implementing Remote Network Monitoring Tools
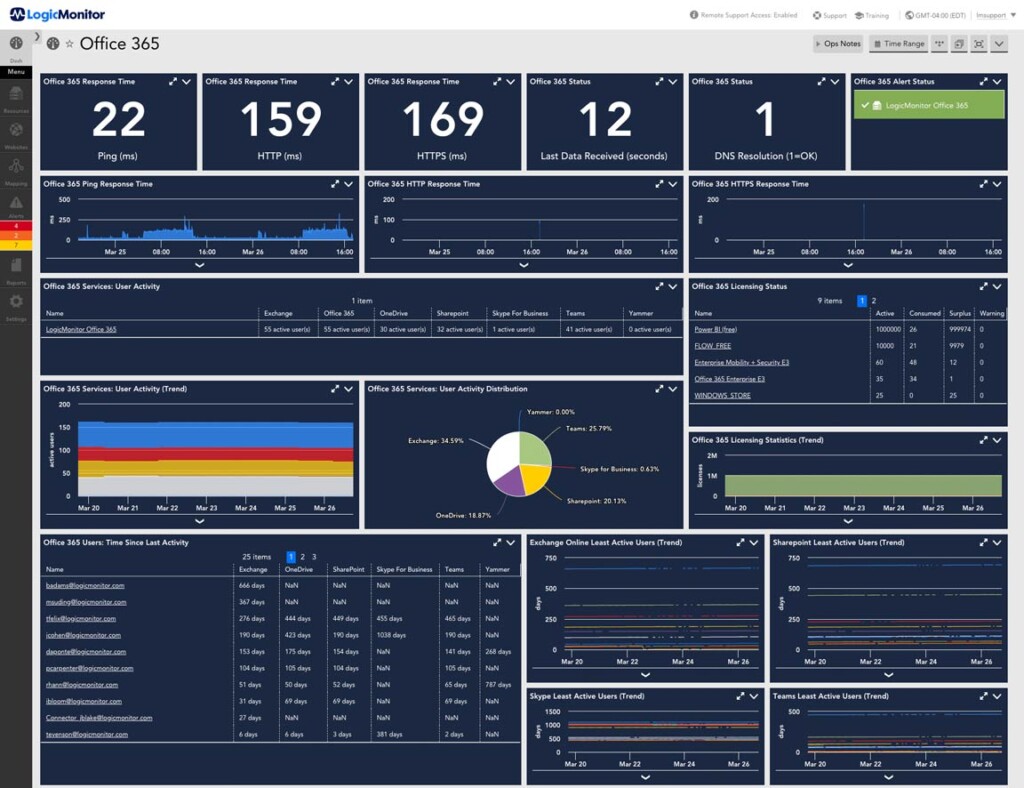
Implementing remote network monitoring tools involves a methodical approach to ensure effective and reliable monitoring of your network infrastructure. The process encompasses installation, configuration, integration, policy definition, and alert setup.
Installation and Configuration
Installing and configuring remote network monitoring tools is the initial step in the implementation process. This involves:
- Downloading and installing the software on a dedicated server or virtual machine.
- Configuring the tool to connect to your network devices, including servers, routers, switches, and firewalls.
- Defining the specific network elements and metrics you want to monitor, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network traffic.
- Setting up user accounts and access permissions to control who can access and manage the monitoring tool.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating the remote network monitoring tool with your existing systems is crucial for comprehensive monitoring. This involves:
- Connecting the tool to your existing systems management platform, such as Active Directory or a ticketing system.
- Configuring the tool to receive and analyze data from other monitoring tools or applications.
- Ensuring that the tool can share data with other systems for reporting and analysis.
Defining Monitoring Policies
Defining clear monitoring policies is essential for ensuring that the tool effectively monitors your network. This involves:
- Establishing thresholds for key metrics, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and network traffic.
- Specifying the frequency of monitoring checks and the duration of data retention.
- Defining the types of events that should trigger alerts, such as exceeding thresholds, system failures, or security breaches.
Setting Up Alerts and Notifications
Setting up alerts and notifications ensures timely notification of network issues. This involves:
- Configuring the tool to send alerts to designated individuals or teams via email, SMS, or other communication channels.
- Defining the severity levels of alerts, such as critical, warning, or informational.
- Customizing the content of alerts to provide specific information about the issue, including the affected device, the metric that triggered the alert, and the timestamp of the event.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
- Start with a pilot project: Begin with a small-scale implementation to test the tool’s functionality and identify any potential challenges before deploying it across the entire network.
- Document the configuration: Maintain detailed documentation of the tool’s configuration and settings to facilitate troubleshooting and future updates.
- Regularly review and update policies: Regularly review and update monitoring policies to reflect changes in your network infrastructure, security requirements, and business needs.
- Conduct periodic testing: Conduct regular tests of the monitoring tool’s functionality to ensure that alerts are triggered accurately and notifications are delivered promptly.
- Provide training to users: Train relevant personnel on how to use the tool and interpret the data it provides.
Remote Network Monitoring Tools for Different Industries
Remote network monitoring tools are essential for businesses across various industries, enabling them to proactively identify and address network issues before they impact operations. These tools provide valuable insights into network performance, security, and user experience, helping organizations maintain uptime, optimize resource utilization, and ensure data security.
Healthcare
Remote network monitoring tools play a crucial role in healthcare by ensuring the reliable operation of critical medical devices and systems.
- Patient Monitoring Systems: Remote network monitoring tools can track the performance of patient monitoring systems, such as heart rate monitors, blood pressure monitors, and ventilators, alerting healthcare providers to any anomalies or potential failures. This proactive approach helps ensure patient safety and improves the quality of care.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Remote network monitoring tools are essential for maintaining the availability and security of EHR systems. They can monitor network traffic, identify potential security threats, and ensure data integrity, protecting sensitive patient information from unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Telemedicine: As telemedicine becomes increasingly prevalent, remote network monitoring tools are crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of video conferencing, data transmission, and other telemedicine applications. These tools can monitor network performance, identify potential latency issues, and ensure high-quality video and audio transmission for remote consultations and procedures.
Finance
Financial institutions heavily rely on robust and secure networks to process transactions, manage data, and maintain customer trust. Remote network monitoring tools are essential for ensuring network stability, security, and compliance with industry regulations.
- Transaction Processing: Remote network monitoring tools can monitor the performance of financial transaction systems, ensuring smooth and timely processing of payments, trades, and other financial transactions. This helps minimize downtime, reduce operational costs, and maintain customer satisfaction.
- Data Security: Financial institutions are prime targets for cyberattacks, making data security paramount. Remote network monitoring tools can detect and respond to security threats, monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, and enforce security policies to protect sensitive financial data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Compliance: Financial institutions are subject to strict regulations, such as PCI DSS for payment card processing. Remote network monitoring tools help organizations comply with these regulations by providing detailed network performance data, security logs, and compliance reports. This ensures regulatory compliance and minimizes the risk of penalties or fines.
Education
Remote network monitoring tools are essential for educational institutions to ensure the smooth operation of online learning platforms, student data management systems, and other critical IT infrastructure.
- Online Learning Platforms: Remote network monitoring tools can monitor the performance of online learning platforms, ensuring seamless access to course materials, video lectures, and online assessments for students. This helps maintain student engagement and learning outcomes.
- Student Data Management: Educational institutions must protect student data, including personal information, academic records, and financial data. Remote network monitoring tools can monitor network traffic, detect security threats, and ensure data integrity, protecting student data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Network Optimization: Remote network monitoring tools can help educational institutions optimize network performance, ensuring smooth internet access for students, faculty, and staff. This helps minimize network latency, improve application responsiveness, and enhance the overall online learning experience.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies rely on complex networks to manage production processes, control equipment, and collect data from sensors and machines. Remote network monitoring tools are essential for ensuring network stability, security, and the smooth operation of production lines.
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS): Remote network monitoring tools can monitor the performance of industrial control systems, ensuring the reliable operation of machinery and equipment. This helps prevent downtime, reduce production costs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Data Acquisition and Analysis: Manufacturing companies collect vast amounts of data from sensors and machines. Remote network monitoring tools can monitor data flow, ensure data integrity, and provide insights into production processes, helping optimize efficiency and reduce waste.
- Security: Manufacturing companies are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can disrupt production, compromise data, and cause significant financial losses. Remote network monitoring tools can detect and respond to security threats, monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, and enforce security policies to protect critical infrastructure from cyberattacks.
Retail
Retail businesses rely on networks to manage point-of-sale (POS) systems, inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and other critical applications. Remote network monitoring tools are essential for ensuring network stability, security, and the smooth operation of retail operations.
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: Remote network monitoring tools can monitor the performance of POS systems, ensuring smooth and reliable transaction processing. This helps minimize downtime, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Inventory Management: Remote network monitoring tools can monitor the performance of inventory management systems, ensuring accurate tracking of stock levels, order fulfillment, and supply chain operations. This helps optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and improve overall efficiency.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Remote network monitoring tools can monitor the performance of CRM systems, ensuring seamless customer interactions, data management, and marketing campaigns. This helps improve customer service, build loyalty, and drive sales.
The Future of Remote Network Monitoring
Remote network monitoring is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the changing demands of modern businesses. The future of this field is bright, with exciting developments poised to revolutionize how we manage and secure our networks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming the way we approach network monitoring. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these technologies can identify patterns, predict anomalies, and automate tasks that were previously done manually.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze network performance data to anticipate potential issues and schedule maintenance before they cause outages. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and reduces costs.
- Threat Detection: AI-powered security systems can detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time, identifying suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Automated Remediation: AI can automate the process of resolving network issues, reducing the need for human intervention and accelerating recovery times.
Cloud-Based Monitoring Solutions
Cloud-based monitoring solutions offer several advantages over traditional on-premises systems. They are scalable, cost-effective, and provide access to advanced features and functionalities.
- Scalability: Cloud solutions can easily scale to accommodate growing network demands, ensuring that you have the resources you need when you need them.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based monitoring eliminates the need for expensive hardware and software investments, making it a more affordable option for businesses of all sizes.
- Accessibility: Cloud solutions provide remote access to monitoring data, allowing you to manage your network from anywhere with an internet connection.
Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration are key to simplifying network management and improving efficiency. These technologies allow you to automate repetitive tasks, such as provisioning new devices, configuring network settings, and responding to alerts.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automation frees up IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks, such as network optimization and security planning.
- Increased Consistency: Automated processes ensure that tasks are performed consistently, reducing the risk of human error.
- Faster Response Times: Automated workflows enable faster response times to network events, minimizing downtime and improving service availability.
Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
The increasing adoption of IoT devices is creating new challenges for network monitoring. Remote network monitoring tools are evolving to support the unique needs of IoT environments.
- Device Management: IoT devices require centralized management and monitoring to ensure their security and performance. Remote network monitoring tools provide the necessary capabilities to manage large-scale IoT deployments.
- Data Analytics: IoT devices generate vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to gain valuable insights into network performance and user behavior. Remote network monitoring tools can help you leverage this data to improve network efficiency and optimize resource allocation.
- Security: IoT devices are often vulnerable to security threats. Remote network monitoring tools can help you identify and mitigate these threats, ensuring the security of your IoT ecosystem.
Security Considerations for Remote Network Monitoring: Remote Network Monitoring Tools
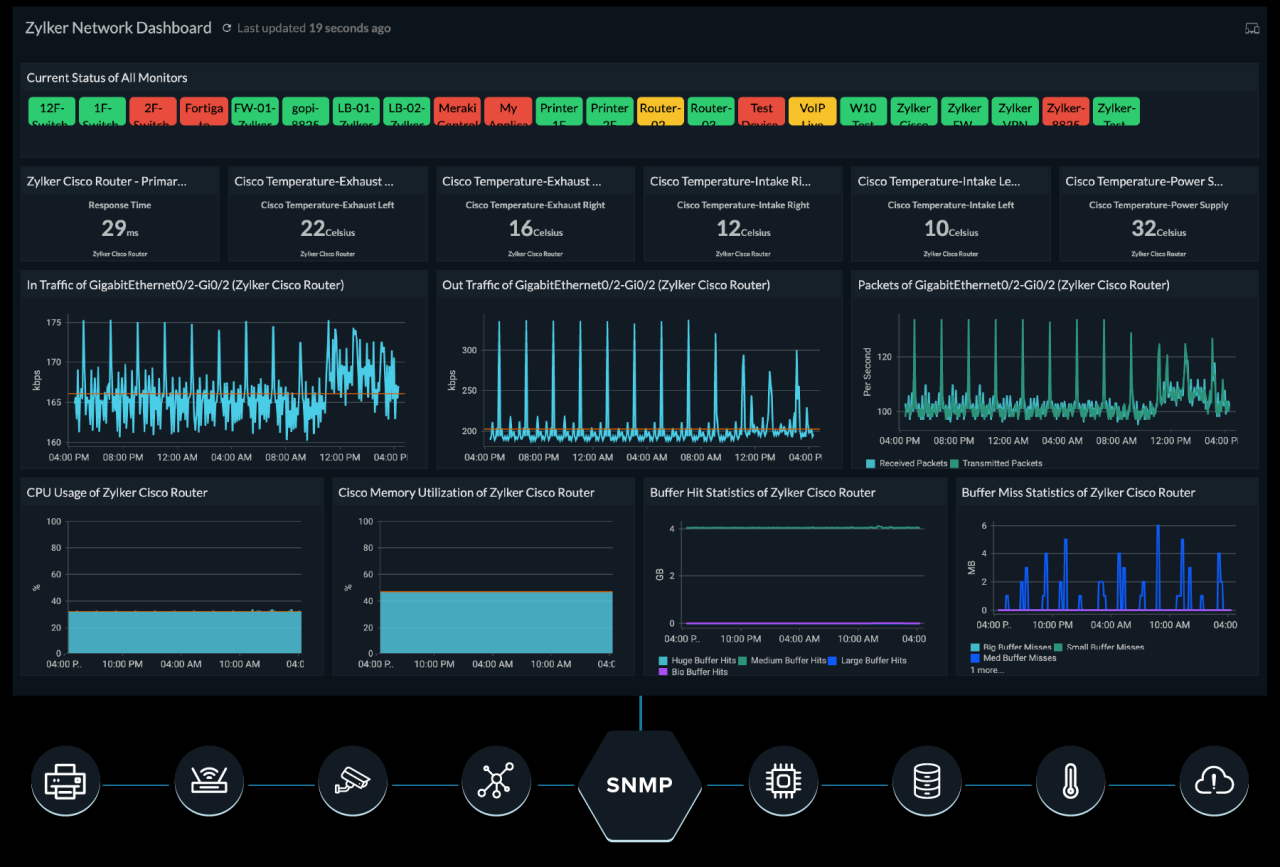
Remote network monitoring tools are powerful tools that can provide valuable insights into the health and performance of your network. However, they also introduce security risks that must be addressed to protect your data and systems.
Access Control and Authentication
Secure access control and robust authentication mechanisms are crucial for protecting your remote network monitoring systems. This involves implementing measures to restrict access to authorized personnel and verifying their identities before granting them access.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile app. This makes it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to your monitoring systems.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): RBAC assigns different levels of access to users based on their roles and responsibilities. This ensures that users can only access the data and functions they need to perform their jobs, minimizing the risk of unauthorized actions.
- Strong passwords and password policies: Enforce strong password policies that require users to create complex passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Regularly encourage password changes to enhance security.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive network data transmitted between your monitoring tools and your systems. This involves converting data into an unreadable format that can only be accessed with a decryption key.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): TLS/SSL encrypts data during transmission, preventing eavesdropping and data interception. Ensure that your monitoring tools and systems support TLS/SSL encryption.
- Data at rest encryption: Encrypt data stored on your monitoring systems’ servers and databases to protect it from unauthorized access even if the physical servers are compromised.
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your remote network monitoring systems. These audits should be conducted by qualified security professionals and should cover all aspects of your systems, including access control, data encryption, and system configurations.
- Vulnerability scanning: Use automated tools to scan your systems for known vulnerabilities and security holes. This helps identify potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
- Penetration testing: Engage a team of ethical hackers to simulate real-world attacks on your systems. This helps identify weaknesses that might be missed by vulnerability scans and provides valuable insights into how attackers might attempt to compromise your systems.
Patch Management
Keeping your remote network monitoring tools and systems up to date with the latest security patches is crucial for mitigating vulnerabilities. Security patches address known vulnerabilities and weaknesses, reducing the risk of attacks.
- Automated patch management: Implement automated patch management systems to ensure that all systems are patched promptly and consistently. This reduces the time it takes to apply patches and minimizes the risk of systems being vulnerable to attacks.
- Regularly review and update patch management policies: Regularly review and update your patch management policies to ensure that they are effective and up-to-date with the latest security best practices.
Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Remote network monitoring tools can be vulnerable to various security threats, including:
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: These attacks aim to overwhelm your monitoring systems with traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate users. Mitigation strategies include implementing rate limiting, using firewalls, and having a robust disaster recovery plan.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks: These attacks involve an attacker intercepting communication between your monitoring tools and your systems, potentially stealing sensitive data or injecting malicious code. Mitigation strategies include using TLS/SSL encryption, verifying the authenticity of websites and applications, and educating users about the risks of MitM attacks.
- Unauthorized access: Unauthorized access to your monitoring systems can lead to data breaches, system modifications, and other security incidents. Mitigation strategies include implementing strong access control measures, regularly monitoring system logs, and using intrusion detection systems.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Remote network monitoring tools have become essential for businesses of all sizes. These tools offer real-time visibility into network performance, security, and user activity, enabling organizations to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact business operations. To illustrate the real-world impact of these tools, let’s explore some case studies.
Case Study: Retail Giant Improves Customer Experience
This retail giant faced challenges with slow website loading times and frequent network outages, impacting customer experience and sales. They implemented a remote network monitoring tool that provided real-time insights into network performance, identifying bottlenecks and performance issues. By analyzing the data, they discovered that their network infrastructure was overloaded during peak shopping hours. The company addressed this issue by upgrading their network equipment and optimizing their website for peak traffic. The results were significant: website loading times improved by 30%, network outages were reduced by 50%, and customer satisfaction scores increased by 15%.
Case Study: Financial Institution Enhances Security Posture
This financial institution was concerned about the increasing threat of cyberattacks and sought to strengthen its security posture. They implemented a remote network monitoring tool that provided comprehensive security insights, including threat detection, vulnerability assessment, and intrusion prevention. The tool identified and mitigated several security vulnerabilities, including outdated software, weak passwords, and unauthorized access attempts. As a result, the financial institution successfully prevented several cyberattacks, protecting sensitive customer data and ensuring business continuity.
Case Study: Healthcare Provider Improves Patient Care
This healthcare provider faced challenges with slow network performance, impacting patient care and administrative operations. They implemented a remote network monitoring tool that provided real-time insights into network performance, identifying issues that were affecting critical medical applications. The tool helped them identify and resolve network bottlenecks, resulting in improved patient care, faster diagnosis and treatment, and increased efficiency in administrative tasks. The healthcare provider reported a 20% reduction in patient wait times and a 15% increase in patient satisfaction scores.
Final Thoughts
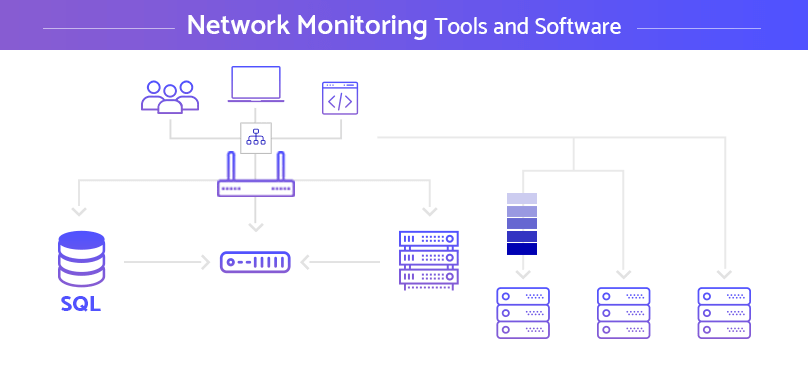
By embracing remote network monitoring tools, organizations can gain valuable insights into their network’s health and performance, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that enhance security, optimize efficiency, and ultimately drive business success. As technology continues to evolve, remote network monitoring tools will play an even more critical role in navigating the complexities of the modern digital landscape.
Remote network monitoring tools are essential for maintaining a healthy and secure network. They provide real-time insights into network performance, allowing you to identify and resolve issues before they impact users. Many of these tools offer detailed documentation that can be downloaded as PDFs, such as the ones available at pdf free download.
These documents can be incredibly helpful for understanding the intricacies of specific tools and maximizing their potential.