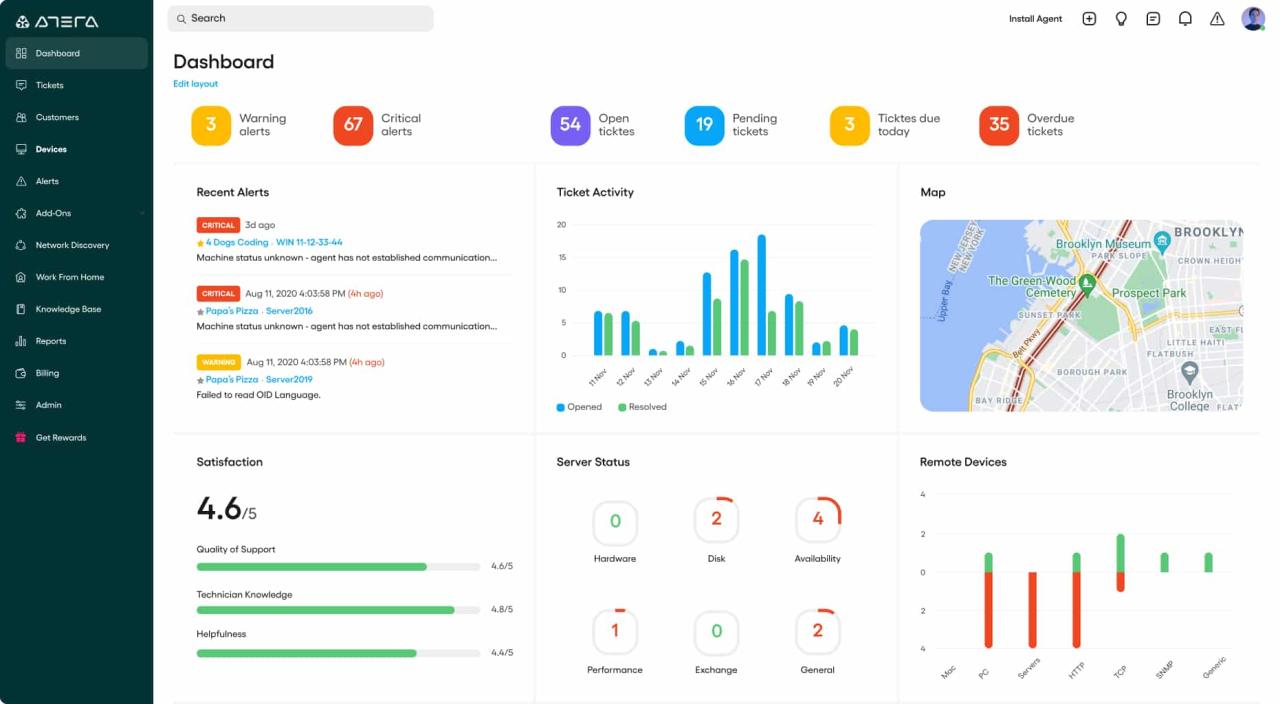
Remote monitoring tools are the unsung heroes of the digital world, quietly safeguarding our systems and ensuring seamless operations. These powerful tools provide a real-time window into the health and performance of our networks, servers, and applications, enabling us to proactively identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where your website crashes without warning, your server experiences crippling slowdowns, or your network suffers from intermittent outages. Remote monitoring tools act as vigilant guardians, constantly analyzing data streams and triggering alerts when anomalies arise, allowing us to swiftly diagnose and resolve problems before they impact our users or businesses.
Introduction to Remote Monitoring Tools
Remote monitoring tools are software applications that allow users to remotely monitor and manage various systems, devices, and processes. They provide real-time insights into the performance, health, and security of these assets, enabling proactive issue identification and resolution.
The use of remote monitoring tools offers numerous benefits for businesses and individuals alike. They provide a centralized view of operations, enabling efficient management and timely responses to potential issues. Remote monitoring tools also enhance security by detecting and alerting users to potential threats, allowing for swift mitigation measures.
Types of Remote Monitoring Tools
Remote monitoring tools come in various forms, each designed to address specific monitoring needs. Some common types include:
- Network Monitoring Tools: These tools monitor network performance, identify bottlenecks, and track traffic patterns. Examples include SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, PRTG Network Monitor, and ManageEngine OpManager.
- Server Monitoring Tools: These tools monitor the health and performance of servers, including CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and system uptime. Popular examples include Datadog, New Relic, and Prometheus.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM) Tools: These tools monitor the performance of applications, identifying slowdowns, errors, and bottlenecks. Examples include Dynatrace, AppDynamics, and Instana.
- Security Monitoring Tools: These tools monitor for security threats, such as malware, intrusion attempts, and data breaches. Examples include Splunk, AlienVault OSSIM, and LogRhythm.
- Cloud Monitoring Tools: These tools monitor the performance and health of cloud infrastructure, including virtual machines, databases, and storage services. Examples include CloudWatch (AWS), Stackdriver (Google Cloud), and Azure Monitor (Microsoft Azure).
Key Features of Remote Monitoring Tools

Remote monitoring tools are essential for businesses and individuals alike, enabling them to keep a close eye on their systems, networks, and devices, regardless of location. These tools provide a comprehensive suite of features that empower users to manage their assets effectively, ensure optimal performance, and proactively address potential issues.
Real-Time Data Monitoring and Alerts
Real-time data monitoring is a cornerstone of remote monitoring tools. These tools constantly collect data from various sources, including servers, applications, networks, and physical devices. This data is then processed and presented in a user-friendly interface, providing a comprehensive overview of system health and performance.
Real-time monitoring enables users to stay informed about critical system metrics, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network bandwidth. It also facilitates the detection of anomalies and potential problems.
Many remote monitoring tools offer customizable alerts that notify users of specific events or conditions. These alerts can be triggered by various factors, such as:
- Exceeding predefined thresholds for critical metrics (e.g., CPU usage exceeding 90%)
- Detecting unusual patterns in data (e.g., sudden spikes in network traffic)
- Identifying specific events (e.g., system crashes, application errors)
Alerts can be delivered through various channels, including email, SMS, and push notifications, ensuring that users are promptly informed of any critical issues.
Performance Analysis
Remote monitoring tools play a vital role in performance analysis by providing detailed insights into system behavior. These insights help users identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall system efficiency.
Remote monitoring tools often include advanced reporting and visualization features that allow users to analyze data trends over time. These features enable users to:
- Identify areas of improvement by pinpointing resource-intensive processes or applications.
- Track performance metrics over time, allowing for trend analysis and proactive optimization.
- Compare performance across different systems or time periods, facilitating performance benchmarking.
By leveraging performance analysis capabilities, users can make informed decisions about resource allocation, system upgrades, and performance optimization strategies.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Remote monitoring tools are invaluable for troubleshooting and diagnostics. They provide a wealth of data that helps users quickly pinpoint the root cause of issues and resolve them efficiently.
Key features that facilitate troubleshooting and diagnostics include:
- Log analysis: Remote monitoring tools can collect and analyze system logs, providing insights into system events, errors, and warnings.
- Performance profiling: By tracking resource usage, these tools can identify specific processes or applications that are causing performance issues.
- Network monitoring: Remote monitoring tools can monitor network traffic, identify bottlenecks, and diagnose network connectivity problems.
By leveraging these features, users can quickly diagnose problems, identify potential solutions, and resolve issues efficiently.
Types of Remote Monitoring Tools
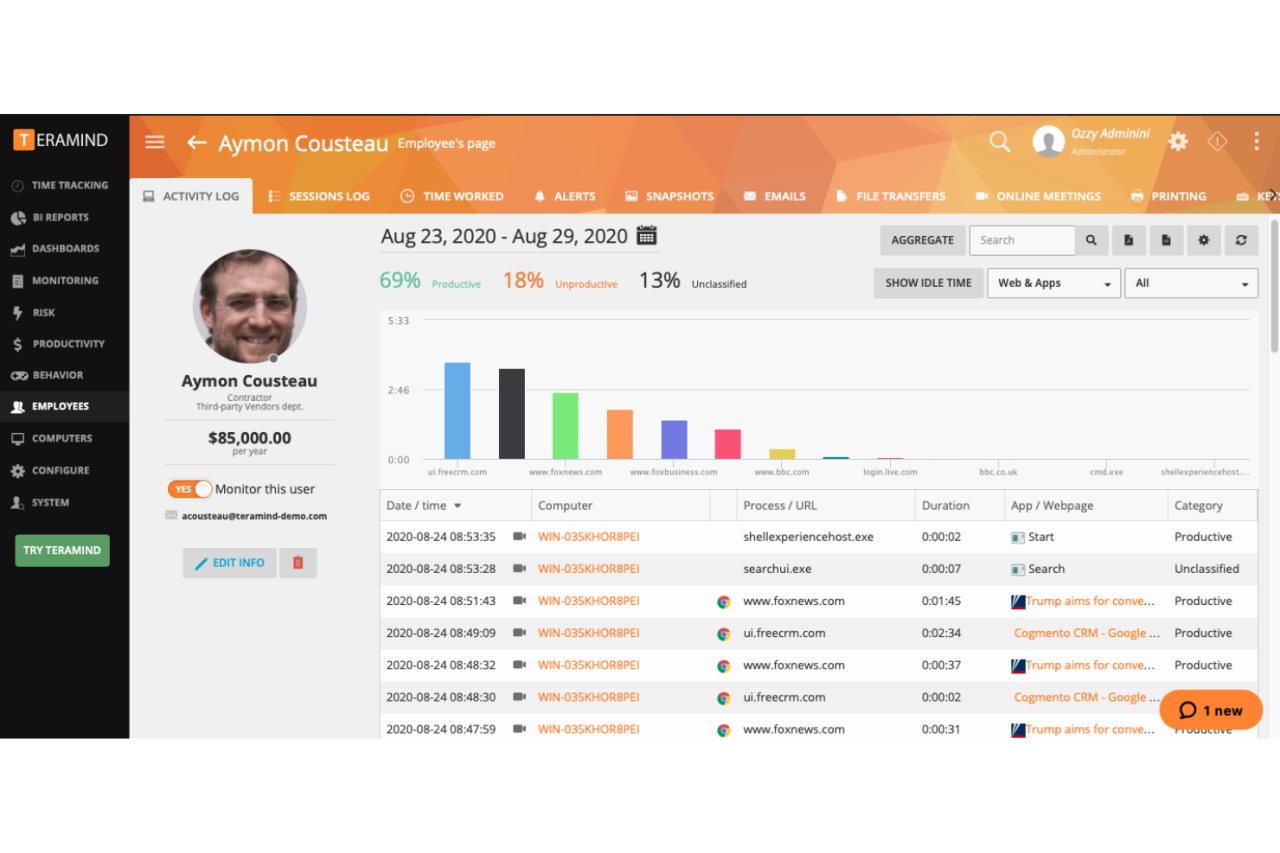
Remote monitoring tools can be broadly categorized based on their applications, allowing for focused solutions tailored to specific needs. These categories represent different aspects of system health and performance, each with unique features and functionalities.
Network Monitoring Tools
Network monitoring tools play a crucial role in maintaining the health and performance of your network infrastructure. These tools continuously monitor network traffic, identify potential bottlenecks, and alert administrators to any issues that may arise.
- Traffic Analysis: Network monitoring tools provide detailed insights into network traffic patterns, identifying bandwidth usage trends, identifying potential bottlenecks, and understanding application performance.
- Performance Metrics: They track key performance indicators (KPIs) like latency, packet loss, and jitter, allowing administrators to assess network health and identify areas for improvement.
- Security Monitoring: These tools can detect suspicious network activity, identify potential security threats, and alert administrators to potential breaches or intrusions.
- Troubleshooting: Network monitoring tools facilitate efficient troubleshooting by providing real-time visibility into network activity, helping pinpoint the root cause of network issues.
Server Monitoring Tools
Server monitoring tools provide a comprehensive view of server performance and resource utilization, ensuring optimal operation and preventing potential downtime.
- Resource Utilization: These tools monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and other critical server resources, providing insights into resource allocation and potential performance bottlenecks.
- Service Availability: Server monitoring tools ensure the availability of critical services by monitoring their uptime and alerting administrators to any service outages or interruptions.
- Performance Optimization: By analyzing server performance data, administrators can identify areas for optimization, improving server efficiency and overall system performance.
- Security Monitoring: Server monitoring tools can detect suspicious activity on servers, identify potential security vulnerabilities, and alert administrators to any security threats.
Application Performance Monitoring Tools
Application performance monitoring (APM) tools provide insights into the performance and health of applications, helping identify and resolve performance bottlenecks and ensure a smooth user experience.
- Performance Metrics: APM tools track key metrics like response times, error rates, and transaction throughput, providing insights into application performance and user experience.
- Code Profiling: Some APM tools offer code profiling capabilities, allowing developers to identify performance bottlenecks within application code and optimize its performance.
- Real-User Monitoring: These tools track the performance of applications from the perspective of end users, providing insights into user experience and identifying potential issues that impact users.
- Troubleshooting: APM tools provide detailed insights into application behavior, facilitating efficient troubleshooting and identifying the root cause of performance issues.
Cloud-Based Monitoring Tools
Cloud-based monitoring tools offer a scalable and flexible approach to monitoring various aspects of cloud infrastructure, applications, and services.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: These tools monitor the health and performance of cloud infrastructure components like virtual machines, storage, and networking, ensuring optimal cloud resource utilization.
- Application Monitoring: Cloud-based monitoring tools provide insights into the performance and health of cloud-native applications, including containerized applications and serverless functions.
- Security Monitoring: These tools can detect suspicious activity within cloud environments, identify potential security vulnerabilities, and alert administrators to any security threats.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud-based monitoring tools provide insights into cloud resource consumption, helping organizations optimize cloud spending and reduce unnecessary costs.
Benefits of Remote Monitoring Tools
Remote monitoring tools offer a range of advantages that can significantly enhance operational efficiency, system reliability, and cost optimization. By providing real-time insights into system performance and potential issues, these tools empower organizations to proactively address problems, optimize resource utilization, and improve overall business outcomes.
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Remote monitoring tools play a crucial role in boosting efficiency and productivity by streamlining processes, reducing downtime, and enabling proactive issue resolution.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: These tools can automatically generate alerts and notifications when predefined thresholds are breached, enabling prompt action and minimizing potential disruptions. This proactive approach helps reduce the time spent on manual monitoring and troubleshooting, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic tasks.
- Real-time Performance Monitoring: Real-time monitoring dashboards provide a comprehensive view of system performance, enabling quick identification of bottlenecks and performance degradation. This information allows for timely optimization and resource allocation, ensuring optimal system performance and maximizing productivity.
- Centralized Monitoring Platform: Remote monitoring tools offer a centralized platform for managing multiple systems and devices, simplifying monitoring and reducing administrative overhead. This consolidated view provides a comprehensive understanding of the entire IT infrastructure, facilitating faster problem identification and resolution.
Impact on System Availability and Reliability
Remote monitoring tools significantly contribute to improving system availability and reliability by enabling early detection and resolution of issues, minimizing downtime, and ensuring continuous operation.
- Proactive Issue Detection: By continuously monitoring system metrics and performance indicators, remote monitoring tools can detect potential issues before they escalate into major problems. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted service delivery.
- Reduced Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): Remote monitoring tools facilitate faster problem identification and resolution by providing detailed system information and historical data. This allows IT teams to quickly diagnose issues and implement appropriate solutions, minimizing the impact of outages and downtime.
- Improved Service Level Agreements (SLAs): By ensuring high system availability and reliability, remote monitoring tools contribute to meeting and exceeding service level agreements (SLAs). This improves customer satisfaction and builds trust in the organization’s ability to deliver consistent and reliable services.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Remote monitoring tools contribute to cost reduction and resource optimization by streamlining operations, minimizing downtime, and enabling efficient resource allocation.
- Reduced Downtime Costs: By enabling proactive issue detection and resolution, remote monitoring tools minimize downtime, reducing the associated costs of lost productivity, customer dissatisfaction, and revenue loss. This can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Remote monitoring tools provide real-time insights into resource usage, allowing for efficient allocation and optimization. This ensures that resources are utilized effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- Reduced IT Staff Costs: By automating monitoring and alerting tasks, remote monitoring tools free up IT staff to focus on higher-value activities, such as system optimization, strategic planning, and innovation. This can lead to reduced staffing costs and improved overall efficiency.
Proactive Maintenance and Problem Prevention
Remote monitoring tools play a crucial role in proactive maintenance and problem prevention by providing real-time insights into system health, enabling predictive analytics, and facilitating timely intervention.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, remote monitoring tools can predict potential failures and proactively schedule maintenance. This helps prevent unexpected downtime and extends the lifespan of critical equipment.
- Performance Optimization: Real-time monitoring data allows for continuous performance optimization, ensuring optimal system performance and reducing the risk of performance bottlenecks. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and improves overall system efficiency.
- Security Monitoring: Remote monitoring tools can be used to monitor security events and detect potential threats. This proactive approach helps identify and address security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring system security.
Implementing Remote Monitoring Tools
Implementing remote monitoring tools involves a series of steps to ensure effective and seamless integration into your existing infrastructure. This process involves configuring agents and sensors, defining thresholds and alerts, and integrating the tools with your existing systems.
Configuring Monitoring Agents and Sensors
Configuring monitoring agents and sensors is crucial for collecting data from monitored systems. This involves installing agents on target systems and configuring them to collect the desired data.
- Agent Installation: Agents are software programs installed on the target systems to collect data. The installation process typically involves downloading the agent software from the remote monitoring tool provider and running the installer.
- Sensor Configuration: Sensors are specific components within agents that collect specific types of data, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, or network traffic. You can configure sensors to monitor specific metrics and define how often they should collect data.
- Data Collection and Transmission: Once configured, agents collect data from the target systems and transmit it to the remote monitoring tool’s central server for analysis and reporting.
Defining Monitoring Thresholds and Alerts
Monitoring thresholds and alerts help you define critical levels for monitored metrics and receive notifications when these thresholds are exceeded. This enables proactive problem identification and timely intervention.
- Threshold Definition: Thresholds are predefined values for monitored metrics. When a metric exceeds or falls below its threshold, the monitoring tool triggers an alert. You can define different thresholds for different metrics based on your specific requirements and tolerance levels.
- Alert Configuration: Alerts are notifications sent to designated recipients when a threshold is exceeded. You can configure the type of alert (email, SMS, push notification), the recipient list, and the severity level of the alert.
- Alert Escalation: You can also configure alert escalation mechanisms, which automatically escalate alerts to higher-level personnel if the initial alert remains unresolved for a specific duration.
Integrating Remote Monitoring Tools with Existing Systems
Integrating remote monitoring tools with existing systems is crucial for a holistic view of your infrastructure. This allows you to correlate data from different systems and gain deeper insights into your environment.
- API Integration: Many remote monitoring tools provide APIs that allow you to integrate them with other systems. This enables data exchange and automated actions based on monitoring data.
- Log Integration: Integrating remote monitoring tools with your log management systems allows you to correlate monitoring data with system logs, providing a comprehensive view of events and potential issues.
- Ticketing System Integration: Integrating remote monitoring tools with your ticketing system automatically creates tickets when alerts are triggered, streamlining incident management and resolution processes.
Security Considerations for Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring tools offer significant advantages for businesses, but they also introduce security vulnerabilities that require careful consideration. Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of monitored systems.
Potential Security Risks
Remote monitoring tools can be susceptible to various security risks, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and system disruptions.
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in the remote monitoring system or gain access through compromised credentials, allowing them to view, modify, or delete sensitive data.
- Data Breaches: Data transmitted between the monitoring system and the monitored devices could be intercepted or stolen by attackers, exposing confidential information to unauthorized parties.
- System Disruptions: Attackers could attempt to disable or disrupt the remote monitoring system, impacting the ability to monitor critical systems and respond to incidents.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Attackers could flood the remote monitoring system with traffic, overwhelming its resources and preventing legitimate users from accessing it.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Monitoring Systems
Implementing strong security measures is critical to mitigating these risks and protecting sensitive data.
- Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Employ strong, unique passwords for all user accounts and enable multi-factor authentication to enhance security.
- Regularly Update Software: Keep the remote monitoring software, operating systems, and any other related applications up to date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Isolate the remote monitoring system from other networks to limit the impact of a potential breach.
- Enable Secure Communication Protocols: Use secure communication protocols such as HTTPS and SSH to encrypt data transmitted between the monitoring system and monitored devices.
- Implement Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Deploy IDS/IPS solutions to detect and prevent malicious activity on the network.
- Regularly Monitor Security Logs: Review security logs for suspicious activity and promptly investigate any anomalies.
- Train Users on Security Best Practices: Educate users about security risks and best practices for using remote monitoring tools.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption and access control are crucial components of securing remote monitoring systems.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement granular access control policies to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions.
Mitigating Security Threats
Several measures can be taken to mitigate security threats and protect remote monitoring systems.
- Security Audits: Regularly conduct security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security best practices.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and test an incident response plan to address security incidents effectively and minimize potential damage.
- Use a Reputable Vendor: Choose a reputable vendor that provides secure remote monitoring solutions and adheres to industry security standards.
Best Practices for Effective Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring tools are powerful instruments for maintaining system health and performance. However, their effectiveness hinges on how well they are implemented and utilized. Optimizing configurations, establishing clear goals, and interpreting data effectively are crucial aspects of maximizing the value of remote monitoring.
Optimizing Remote Monitoring Configurations
Optimizing configurations ensures that the monitoring system effectively captures the necessary data and alerts promptly to potential issues. This involves tailoring the monitoring system to the specific needs of your environment.
- Define Monitoring Scope: Determine which systems, applications, and metrics are essential to monitor. Focus on critical components and prioritize those that have the most significant impact on business operations.
- Configure Alerts: Set appropriate alert thresholds based on the acceptable performance levels for each metric. For example, define specific CPU utilization limits or disk space thresholds that trigger alerts. Consider using different alert levels (e.g., warning, critical) to prioritize issues.
- Optimize Monitoring Frequency: Balance the need for frequent updates with the potential performance impact of excessive monitoring. For critical metrics, frequent monitoring is crucial. However, less critical metrics might be monitored less frequently to reduce the load on the system.
- Minimize Noise: Filter out irrelevant data and unnecessary alerts to avoid overwhelming the monitoring team. This involves carefully configuring alert rules and establishing a process for managing false positives.
Establishing Clear Monitoring Goals and Objectives
Clear goals and objectives provide direction and ensure that monitoring efforts are aligned with business priorities.
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define the metrics that directly impact business success. Examples include website uptime, application response times, and server resource utilization.
- Set Performance Targets: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each KPI. For example, aim for 99.9% website uptime or a maximum response time of 2 seconds for critical applications.
- Align Monitoring with Business Objectives: Ensure that monitoring efforts support the organization’s overall goals. For example, if the goal is to improve customer satisfaction, monitor metrics related to application performance and website availability.
Analyzing and Interpreting Monitoring Data
Data analysis is crucial for identifying trends, understanding root causes, and making informed decisions.
- Data Visualization: Utilize dashboards and graphs to visualize data effectively. This allows for quick identification of trends, anomalies, and potential issues. Consider using various chart types (e.g., line graphs, bar charts, heatmaps) to represent different data types.
- Correlation Analysis: Examine relationships between different metrics to identify potential dependencies. For example, analyze whether a spike in CPU utilization coincides with an increase in application errors.
- Trend Analysis: Track performance metrics over time to identify patterns and predict potential issues. This allows for proactive maintenance and resource optimization.
Creating Actionable Insights from Monitoring Information
Actionable insights drive improvements and prevent future issues.
- Root Cause Analysis: Use monitoring data to identify the root cause of performance problems. This might involve analyzing logs, reviewing configuration settings, or conducting network analysis.
- Proactive Maintenance: Utilize monitoring data to anticipate and address potential issues before they impact users. This includes scheduling maintenance tasks, upgrading hardware, or optimizing software configurations.
- Performance Optimization: Leverage monitoring data to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. This might involve optimizing code, tuning database settings, or upgrading hardware.
Future Trends in Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring is constantly evolving, driven by the rapid advancements in technology and the growing need for greater efficiency, security, and insights. The integration of emerging technologies, particularly artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), is transforming the landscape of remote monitoring, paving the way for more intelligent and proactive solutions.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies, Remote monitoring tools
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing remote monitoring, enabling more sophisticated and data-driven approaches.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of connected devices generates a massive amount of data, which can be leveraged for real-time monitoring and analysis. IoT sensors and devices can monitor various parameters like temperature, pressure, vibration, and energy consumption, providing valuable insights into the performance and health of assets. This data can be used to predict potential issues and optimize operations, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide scalable and cost-effective infrastructure for remote monitoring systems. They enable remote access to data and applications, facilitating collaboration and streamlining workflows. Cloud-based monitoring solutions offer greater flexibility and agility, allowing businesses to adapt to changing needs and scale their operations seamlessly.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings processing power closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving real-time responsiveness. This is particularly beneficial for remote monitoring applications where immediate action is crucial. Edge devices can perform initial data processing and analysis, sending only relevant information to the cloud for further analysis and decision-making.
- 5G Networks: The advent of 5G networks promises significantly faster data transfer speeds and lower latency, further enhancing real-time remote monitoring capabilities. 5G networks will enable the deployment of more sophisticated and data-intensive monitoring solutions, supporting applications like remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are playing an increasingly vital role in remote monitoring, enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and improved decision-making.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical data and identify patterns to predict potential failures in equipment and systems. This allows for proactive maintenance and repairs, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs. For example, AI can be used to analyze vibration data from a wind turbine to predict when a bearing might fail, allowing for a scheduled maintenance before the failure occurs.
- Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can detect anomalies and deviations from expected behavior in real-time, alerting operators to potential issues. This helps identify problems early on, allowing for prompt intervention and preventing further damage or disruption. For instance, AI can monitor sensor data from a manufacturing process to detect variations in temperature or pressure that might indicate a production defect or malfunction.
- Automated Response: AI-powered systems can automate responses to certain events, reducing human intervention and streamlining operations. This can include tasks like automatically adjusting settings, initiating corrective actions, or escalating issues to the appropriate personnel. For example, AI can be used to automatically adjust the temperature in a data center based on real-time monitoring data, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Data Visualization and Insights: AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data and present it in a user-friendly format, providing actionable insights and facilitating informed decision-making. AI-powered dashboards and visualizations can help operators understand complex data trends and identify areas for improvement. For example, AI can be used to visualize real-time traffic data from a city’s transportation system, identifying congestion points and recommending traffic flow adjustments.
Predictions for the Future of Remote Monitoring
The future of remote monitoring is bright, with exciting advancements on the horizon.
- Increased Automation: Remote monitoring systems will become increasingly automated, relying on AI and ML to perform tasks that were previously handled by humans. This will free up human operators to focus on more strategic and complex tasks, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Security: As remote monitoring systems become more sophisticated and interconnected, security will be paramount. Advancements in cybersecurity technologies will be essential to protect against cyberattacks and ensure the integrity of data and operations.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Remote monitoring solutions will integrate seamlessly with other technologies like blockchain, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) to create more immersive and interactive experiences. For example, AR could be used to overlay real-time monitoring data onto a physical asset, providing operators with a more comprehensive view of its status and performance.
- Personalization and Customization: Remote monitoring solutions will become more personalized and customizable, catering to the specific needs of different industries and applications. This will allow businesses to tailor their monitoring systems to their unique requirements and optimize their operations for maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Remote Monitoring Evolving to Meet Modern Demands
Remote monitoring is evolving to meet the demands of modern systems, which are becoming increasingly complex, interconnected, and data-intensive.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Remote monitoring solutions need to be scalable and flexible to accommodate the growth of data and the expansion of monitored systems. Cloud-based platforms provide the necessary scalability and agility to adapt to changing needs.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: The ability to analyze data in real-time is crucial for timely decision-making and proactive problem-solving. Advancements in edge computing and 5G networks will enable faster data processing and analysis, facilitating real-time monitoring and response.
- Improved User Experience: User-friendly interfaces and intuitive dashboards are essential for making remote monitoring accessible and effective for all users, regardless of their technical expertise. AI-powered tools can simplify data visualization and provide actionable insights, making remote monitoring more intuitive and user-friendly.
- Integration with Business Processes: Remote monitoring solutions need to integrate seamlessly with existing business processes and workflows to maximize their value and impact. This includes integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and other business applications.
Case Studies and Examples: Remote Monitoring Tools
Remote monitoring tools have revolutionized various industries, impacting operational efficiency, cost reduction, and overall productivity. These tools offer real-time insights into systems and processes, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and proactively address potential issues. Let’s explore how remote monitoring tools are being implemented in different sectors and examine some success stories that highlight their effectiveness.
Real-World Applications of Remote Monitoring Tools
Remote monitoring tools are widely adopted across diverse industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, IT, and finance. Here are some specific examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals use remote monitoring systems to track vital signs of patients, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, even from home. This allows for early detection of health complications and timely interventions, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions. For instance, remote patient monitoring systems are used to monitor patients with chronic conditions like heart failure, diabetes, and COPD, allowing healthcare providers to intervene proactively and prevent potential complications.
- Manufacturing: Remote monitoring tools are essential for optimizing production processes in manufacturing facilities. They provide real-time data on machine performance, energy consumption, and material usage, allowing manufacturers to identify inefficiencies and optimize production schedules. For example, remote monitoring systems can be used to track the performance of industrial robots, identify potential malfunctions, and schedule preventative maintenance to minimize downtime and optimize production output.
- IT: IT departments rely heavily on remote monitoring tools to ensure the smooth operation of critical infrastructure, such as servers, networks, and applications. These tools provide real-time alerts about system performance, security threats, and potential outages, allowing IT teams to address issues promptly and prevent downtime. For example, remote monitoring tools can be used to track server utilization, network bandwidth usage, and application performance, enabling IT teams to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize system performance.
- Finance: Financial institutions utilize remote monitoring tools to monitor market trends, customer activity, and fraud detection. These tools provide real-time insights into financial data, enabling organizations to make informed investment decisions, identify potential fraud attempts, and mitigate risks. For instance, remote monitoring systems can be used to track stock market performance, identify suspicious transactions, and detect potential fraud patterns, enabling financial institutions to take timely action to protect their assets and customers.
Impact of Remote Monitoring on Industries
Remote monitoring tools have significantly impacted various industries, driving improvements in operational efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction. Here’s how:
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Remote monitoring provides real-time insights into operations, enabling organizations to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and streamline processes. This leads to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and increased efficiency. For example, in manufacturing, remote monitoring tools can be used to track machine performance and identify potential failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime. In healthcare, remote patient monitoring can help identify potential complications early, allowing for timely interventions and reducing hospital readmissions.
- Cost Reduction: Remote monitoring tools help reduce operational costs by optimizing resource utilization, minimizing downtime, and preventing costly failures. For instance, in manufacturing, remote monitoring systems can be used to optimize energy consumption and reduce waste, resulting in significant cost savings. In IT, remote monitoring tools can help identify potential security threats and prevent costly data breaches.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Remote monitoring tools can improve customer satisfaction by ensuring timely service delivery, proactive problem resolution, and enhanced responsiveness. For example, in the IT sector, remote monitoring tools can help identify and resolve technical issues quickly, minimizing downtime and improving customer experience. In healthcare, remote patient monitoring can provide patients with greater peace of mind and improve their overall well-being.
Success Stories of Remote Monitoring Implementation
Several companies have successfully implemented remote monitoring tools, leading to significant improvements in their operations and overall performance. Here are some notable examples:
- Amazon: Amazon leverages remote monitoring tools extensively to manage its vast network of warehouses and distribution centers. These tools provide real-time data on inventory levels, order fulfillment, and delivery status, enabling Amazon to optimize its logistics operations and ensure efficient delivery of products to customers. This has significantly improved customer satisfaction and reduced delivery times.
- General Electric: GE has implemented remote monitoring systems for its industrial equipment, such as turbines and generators. These systems provide real-time data on equipment performance, allowing GE to identify potential issues early and schedule preventative maintenance, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs. This has significantly improved the reliability and efficiency of GE’s industrial equipment.
- John Deere: John Deere, a leading agricultural equipment manufacturer, has incorporated remote monitoring into its farm machinery. These tools provide real-time data on machine performance, fuel consumption, and location, allowing farmers to optimize their operations and improve efficiency. This has helped farmers to reduce operating costs, increase productivity, and improve crop yields.
Key Case Studies and Their Outcomes
| Case Study | Industry | Key Objectives | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon’s Warehouse Management | E-commerce | Optimize logistics operations, improve customer satisfaction, reduce delivery times. | Significant improvement in customer satisfaction, reduced delivery times, optimized logistics operations. |
| GE’s Industrial Equipment Monitoring | Manufacturing | Improve equipment reliability, reduce maintenance costs, minimize downtime. | Significant improvement in equipment reliability, reduced maintenance costs, minimized downtime. |
| John Deere’s Farm Machinery Monitoring | Agriculture | Optimize farm operations, increase productivity, improve crop yields. | Reduced operating costs, increased productivity, improved crop yields. |
| Hospital’s Remote Patient Monitoring | Healthcare | Improve patient outcomes, reduce hospital readmissions, enhance patient care. | Improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital readmissions, enhanced patient care. |
Closing Notes
In a world increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, remote monitoring tools are indispensable assets. They empower us to maintain optimal system performance, ensure high availability, and minimize downtime, ultimately contributing to a more efficient, reliable, and secure digital experience.
Remote monitoring tools can be invaluable for keeping an eye on your systems, especially when it comes to accessing critical documents. If you’re still using Windows 7, you might need a reliable PDF reader like the one found here.
Once you’ve got your PDF viewing sorted, you can focus on setting up those remote monitoring tools for optimal system security.