QCAD, a powerful and versatile open-source 2D CAD software, empowers users to create technical drawings with precision and ease. This software caters to a diverse audience, including engineers, architects, designers, and hobbyists, offering a comprehensive set of tools for a wide range of projects.
Table of Contents
From its humble beginnings as a personal project, QCAD has evolved into a mature and robust application, boasting a dedicated community of developers and users who contribute to its ongoing development. QCAD’s intuitive interface and extensive feature set make it a compelling choice for anyone seeking a free and reliable solution for 2D design.
QCAD Functionality
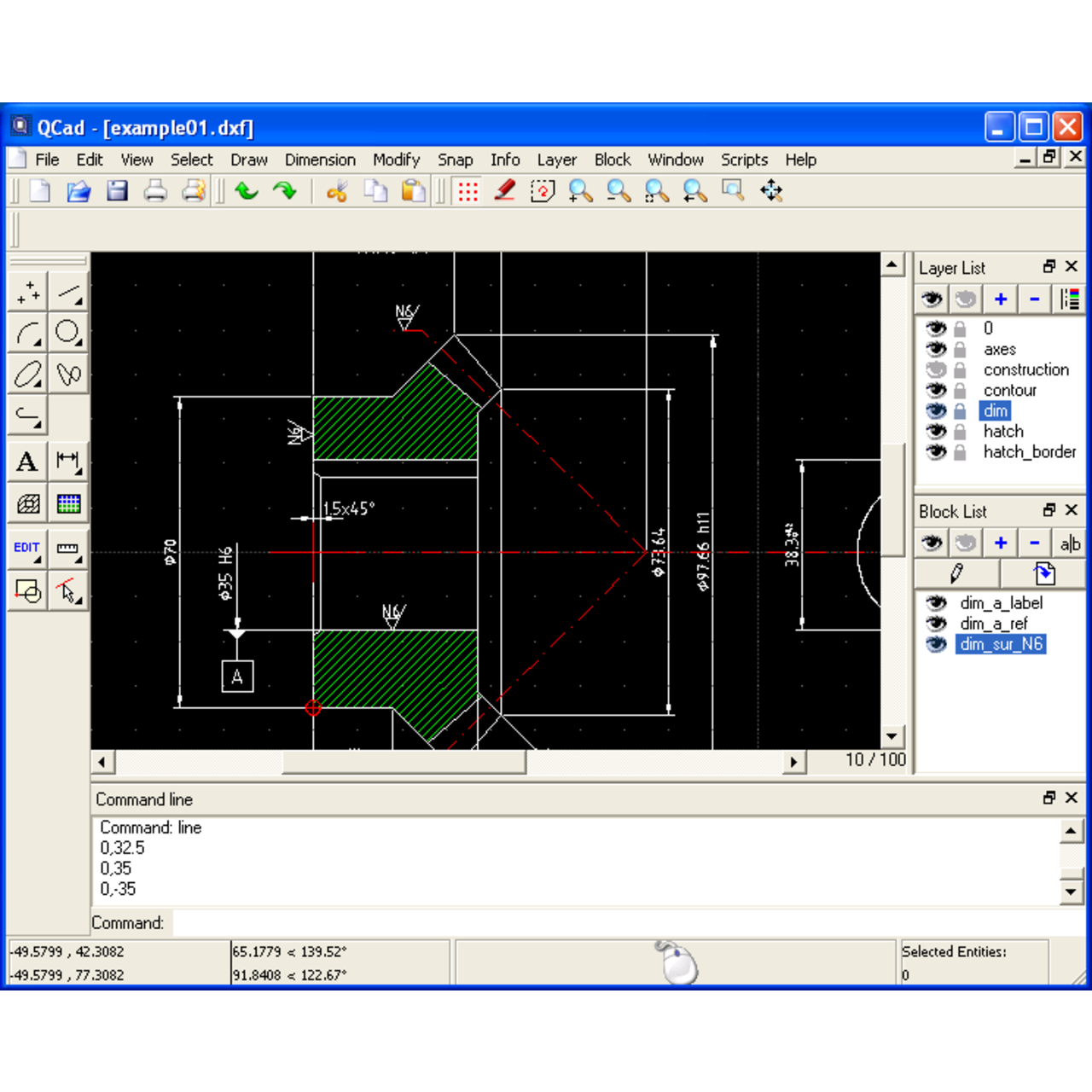
QCAD is a powerful and versatile 2D CAD software that offers a comprehensive set of tools for creating and editing technical drawings. It provides a user-friendly interface and a wide range of features that cater to the needs of both beginners and experienced users.
Drawing Tools
QCAD offers a wide array of drawing tools, enabling users to create various geometric shapes and objects with precision. These tools include:
- Line: Create straight lines with customizable thickness, color, and line styles.
- Arc: Draw circular arcs with specified radius, start and end angles.
- Circle: Create circles with adjustable radius and center point.
- Rectangle: Draw rectangles with customizable dimensions and corner rounding.
- Ellipse: Create ellipses with adjustable major and minor axes.
- Polygon: Draw regular polygons with customizable number of sides and radius.
- Spline: Create smooth curves by defining control points.
- Text: Add text annotations with different fonts, sizes, and styles.
- Hatch: Apply hatch patterns to fill areas with specified angle and spacing.
- Dimension: Create dimensions to specify lengths, angles, and other measurements.
Editing Tools, Qcad
QCAD provides a robust set of editing tools for manipulating and modifying existing drawings. These tools allow users to:
- Move: Move objects to different positions on the drawing.
- Copy: Duplicate objects and paste them at a new location.
- Rotate: Rotate objects around a specified point.
- Scale: Change the size of objects proportionally.
- Mirror: Create a mirror image of an object.
- Trim: Remove portions of objects that intersect with other objects.
- Extend: Extend objects to meet the intersection points with other objects.
- Offset: Create parallel objects at a specified distance from existing objects.
- Fillet: Round off corners of objects with a specified radius.
- Chamfer: Create beveled corners of objects with specified distances.
- Break: Break objects at a specified point.
- Explode: Separate compound objects into individual components.
- Group: Combine multiple objects into a single group for easier manipulation.
- Ungroup: Separate objects that are grouped together.
2D Technical Drawing Capabilities
QCAD is specifically designed for creating 2D technical drawings. Its features and functionalities make it suitable for various applications, including:
- Architectural Drawings: Create floor plans, elevations, and sections for buildings and structures.
- Mechanical Drawings: Design components, assemblies, and machinery.
- Electrical Drawings: Create schematics, wiring diagrams, and circuit layouts.
- Civil Engineering Drawings: Design roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Mapping and Surveying: Create maps, topographic surveys, and property plans.
File Format Support
QCAD supports a wide range of file formats, ensuring compatibility with other CAD software and applications. It can import and export drawings in formats such as:
- DXF (Drawing Exchange Format): A widely used CAD file format that is compatible with many other CAD programs.
- DWG (Drawing): The native file format for Autodesk AutoCAD.
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): A web-based vector graphics format.
- PDF (Portable Document Format): A popular document format that preserves the vector information of the drawing.
- QCAD (QCAD Native Format): The native file format for QCAD, which stores all drawing information in a single file.
QCAD Applications
QCAD is a versatile CAD software that finds application in various industries and professions. Its user-friendly interface, comprehensive features, and affordability make it an ideal choice for both professional and personal use.
Industries and Professions
QCAD is widely used across a broad spectrum of industries and professions. Here are some examples:
- Architecture and Engineering: Architects and engineers use QCAD for creating detailed drawings of buildings, structures, and infrastructure projects. QCAD’s ability to handle complex geometries and generate accurate dimensions makes it suitable for designing intricate structures.
- Mechanical Engineering: Mechanical engineers utilize QCAD for designing and documenting mechanical components, assemblies, and systems. The software’s support for 2D drafting and 3D modeling enables engineers to create precise drawings and visualizations.
- Manufacturing: QCAD is employed in manufacturing industries for creating production drawings, tool designs, and assembly instructions. The software’s compatibility with industry standards ensures seamless integration with manufacturing processes.
- Construction: QCAD is used by construction professionals for creating site plans, building elevations, and construction drawings. Its ability to handle large-scale projects and generate detailed drawings makes it suitable for complex construction projects.
- Education: QCAD is a valuable tool for educators and students in technical fields. It provides a hands-on learning experience for students to develop their CAD skills and gain practical knowledge of technical drawing.
- Hobbyists and Makers: QCAD is accessible to hobbyists and makers who require a powerful and affordable CAD software for their projects. It allows them to design and create custom parts, tools, and prototypes.
Project Examples
QCAD can be used to create a wide range of projects, including:
- Building Plans: QCAD can be used to create detailed building plans, including floor plans, elevations, and sections. This includes residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Mechanical Drawings: QCAD is suitable for creating detailed mechanical drawings, such as component designs, assembly drawings, and exploded views. Examples include gears, bearings, and engine parts.
- Electrical Schematics: QCAD can be used to create electrical schematics for various applications, such as circuit diagrams, wiring diagrams, and control systems. This includes residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems.
- PCB Layout: QCAD can be used for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs), enabling users to create layouts for electronic components and traces.
- Logos and Graphics: QCAD can be used for creating vector-based logos, graphics, and illustrations. This includes corporate logos, product icons, and marketing materials.
Suitability for Different Types of Technical Drawings
QCAD is well-suited for creating various types of technical drawings, including:
- Orthographic Drawings: QCAD excels in creating orthographic drawings, which are multi-view drawings that depict an object from different angles. This is essential for conveying the shape and dimensions of objects accurately.
- Isometric Drawings: QCAD supports the creation of isometric drawings, which provide a three-dimensional representation of an object using parallel lines. This is useful for visualizing the overall shape and dimensions of an object.
- Perspective Drawings: QCAD allows for the creation of perspective drawings, which simulate the way an object appears in real life. This is helpful for creating realistic representations of objects and scenes.
- Schematic Drawings: QCAD can be used for creating schematic drawings, which use symbols and lines to represent electrical, mechanical, or other systems. This is useful for illustrating the relationships between different components.
- Detail Drawings: QCAD is suitable for creating detailed drawings that focus on specific parts or features of an object. This allows for precise representation of dimensions, tolerances, and other important details.
QCAD Installation and Setup
Getting QCAD up and running is straightforward, whether you’re on Windows, macOS, or Linux. This section will guide you through the installation process and provide essential information on system requirements and configuration options.
Installing QCAD on Different Operating Systems
Installing QCAD is a simple process, and the steps are similar across different operating systems.
- Windows: Download the installer from the official QCAD website, run the installer, and follow the on-screen instructions.
- macOS: Download the DMG file from the QCAD website, mount the image, drag the QCAD application to your Applications folder, and you’re ready to go.
- Linux: Most Linux distributions offer QCAD in their package repositories. Use your distribution’s package manager to install it (e.g., apt, yum, dnf). Alternatively, download the source code and compile it yourself.
System Requirements for Running QCAD
QCAD is a relatively lightweight application, but it’s important to meet the minimum system requirements for optimal performance.
- Operating System: Windows 7 or later, macOS 10.10 or later, Linux (various distributions)
- Processor: Intel or AMD processor with at least 1 GHz
- RAM: 2 GB or more is recommended, 4 GB or more is ideal for complex drawings
- Hard Disk Space: 500 MB or more for installation and file storage
- Display: 1024×768 resolution or higher, a higher resolution is recommended for better viewing of drawings
Configuring QCAD for Specific Needs
QCAD offers various configuration options to tailor the software to your specific requirements.
- Units: You can set the units of measurement (e.g., millimeters, inches, feet) for your drawings.
- Grid: Configure the grid settings to suit your design preferences, including grid spacing, line style, and color.
- Layers: Create and manage layers to organize your drawing elements and control their visibility.
- Drawing Templates: Define templates with predefined settings (e.g., units, grid, layers) for consistent drawing creation.
QCAD Resources and Support
Navigating the world of CAD software can be daunting, but QCAD offers a wealth of resources to guide you through your learning journey. Whether you’re a beginner seeking introductory guidance or an experienced user looking for advanced techniques, QCAD provides comprehensive support to empower your design endeavors.
Official Documentation and Tutorials
The official QCAD website is your primary source for comprehensive information and guidance. It houses a robust collection of documentation, tutorials, and user manuals that cover a wide range of topics. You’ll find detailed explanations of QCAD’s features, step-by-step instructions for common tasks, and in-depth guides for more complex operations.
Online Forums and Communities
Beyond the official documentation, a vibrant community of QCAD users thrives online. Forums and online communities offer a platform for sharing knowledge, seeking help, and engaging in discussions with fellow QCAD enthusiasts. These online spaces provide a valuable resource for troubleshooting issues, exchanging tips and tricks, and staying updated on the latest QCAD developments.
Advanced QCAD Techniques
For those seeking to master advanced QCAD techniques, numerous resources are available. Online tutorials, specialized courses, and books delve into more complex aspects of QCAD, such as scripting, macro programming, and advanced drawing techniques. These resources empower you to leverage the full potential of QCAD and create sophisticated designs with ease.
Concluding Remarks: Qcad
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a budding enthusiast, QCAD provides a comprehensive and accessible platform for creating high-quality technical drawings. With its open-source nature, active community, and commitment to continuous improvement, QCAD continues to be a valuable tool for individuals and organizations alike.
QCAD is a powerful and versatile 2D CAD software, offering a range of tools for creating and editing technical drawings. If you find yourself needing to remove QCAD from your system, you can utilize a dedicated uninstaller to ensure a clean and complete removal.
This process helps maintain your system’s stability and prevents any lingering files or configurations from interfering with future installations.

