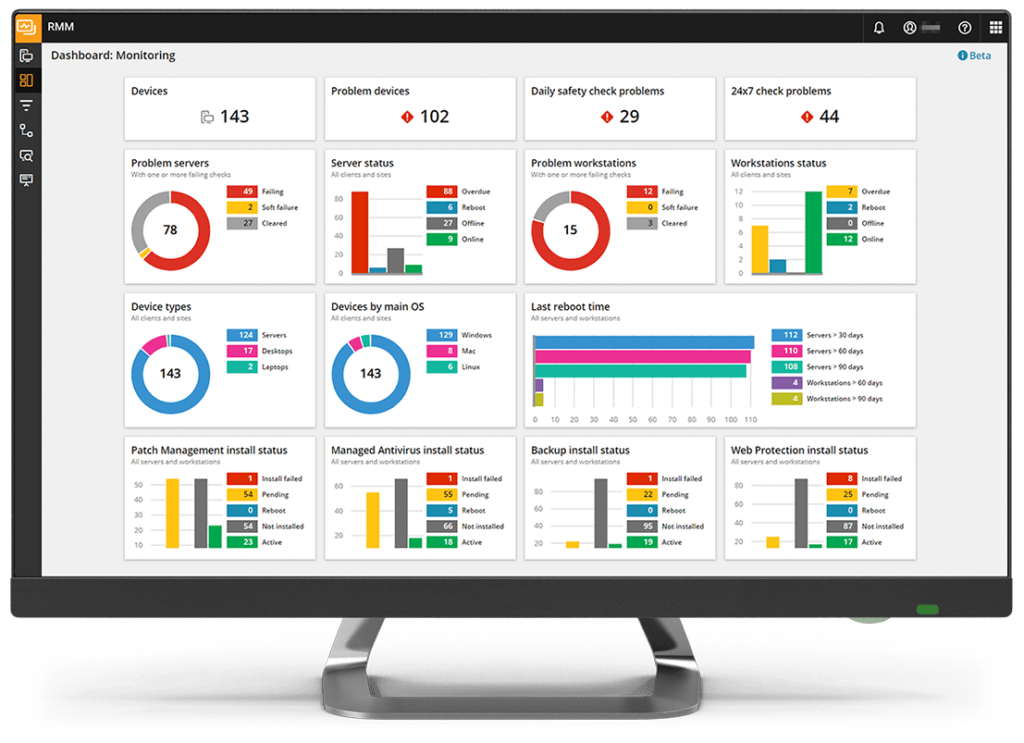
MSP RMM tools set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. MSP RMM tools are a vital component of modern IT management, providing managed service providers (MSPs) with the power to remotely monitor, manage, and secure their clients’ devices and networks. These tools streamline operations, boost efficiency, and enhance client satisfaction, ultimately leading to a more secure and reliable IT environment.
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where MSPs can proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact clients, all while maintaining a high level of security and compliance. This is the reality that MSP RMM tools offer, empowering MSPs to deliver exceptional service and build lasting client relationships.
What is MSP RMM?
MSP RMM stands for Managed Service Provider Remote Monitoring and Management. It is a crucial tool for MSPs (Managed Service Providers) to manage and monitor their clients’ IT infrastructure remotely.
Definition of MSP RMM Tools
MSP RMM tools are software solutions that enable MSPs to remotely monitor and manage their clients’ IT systems, including servers, workstations, applications, and networks. These tools offer a centralized platform for managing multiple client environments, streamlining IT operations, and improving efficiency.
Key Features and Functionalities of MSP RMM Solutions, Msp rmm tools
MSP RMM solutions provide a wide range of features and functionalities to effectively manage client IT infrastructure. These features can be categorized into several key areas:
Monitoring
RMM tools offer comprehensive monitoring capabilities, allowing MSPs to track various aspects of their clients’ IT systems. This includes:
- System performance metrics: CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, network bandwidth, and other critical performance indicators.
- Security events: Intrusion attempts, malware infections, and other security threats.
- Software updates: Patching and vulnerability management to ensure systems are up-to-date and secure.
- Hardware health: Disk health, fan speeds, temperature sensors, and other hardware components.
Management
MSP RMM tools provide a centralized platform for managing and controlling various aspects of client IT systems:
- Remote access: Securely connect to client devices for troubleshooting and support.
- Software deployment: Install, update, and manage software applications across client networks.
- Patching and vulnerability management: Automate software updates and security patches to mitigate risks.
- User management: Create, manage, and control user accounts and permissions on client systems.
- Data backup and recovery: Implement backup strategies and restore data in case of system failures.
Automation
RMM solutions automate repetitive tasks, freeing up MSPs to focus on more strategic initiatives:
- Scheduled tasks: Automate routine maintenance tasks like software updates, antivirus scans, and system reboots.
- Alerting and notifications: Configure alerts for critical events, such as system failures, security breaches, or hardware failures.
- Reporting and analytics: Generate reports on system performance, security events, and other key metrics.
Key Features of MSP RMM Tools
MSP RMM tools are designed to help managed service providers (MSPs) effectively manage and monitor their clients’ IT infrastructure remotely. These tools offer a wide range of features that streamline operations, improve security, and enhance productivity.
Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring capabilities allow MSPs to proactively track the health and performance of their clients’ systems. This feature is crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Real-time System Monitoring: MSP RMM tools provide real-time monitoring of key system metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network activity. This enables MSPs to identify performance bottlenecks and resource constraints, allowing them to address issues before they impact users.
- Hardware Monitoring: MSP RMM tools can monitor the health of hardware components, such as hard drives, RAM, and network cards. This helps MSPs anticipate potential hardware failures and schedule proactive maintenance.
- Software Monitoring: MSP RMM tools can monitor the performance and availability of software applications. This allows MSPs to identify issues with software applications, ensuring smooth operation and minimal downtime.
- Alerts and Notifications: MSP RMM tools generate alerts and notifications when system events or thresholds are triggered. This allows MSPs to be informed about potential issues immediately, enabling them to take prompt action.
Patch Management
Patch management is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, ensuring that systems are protected against known vulnerabilities. MSP RMM tools simplify patch management by automating the process of identifying, downloading, and deploying updates.
- Automated Patch Scanning: MSP RMM tools automatically scan systems for missing or outdated patches, identifying vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
- Patch Deployment: MSP RMM tools can automatically deploy patches to all managed systems, ensuring that systems are up-to-date and protected against the latest threats.
- Patch Scheduling: MSP RMM tools allow MSPs to schedule patch deployments, minimizing disruption to users and ensuring that updates are applied at convenient times.
- Patch Approval and Rollback: MSP RMM tools provide a mechanism for approving or rejecting patch deployments, allowing MSPs to control the update process and ensure compatibility with client systems.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is crucial for protecting client devices from malware, viruses, and other threats. MSP RMM tools offer a range of features that enhance endpoint security, including:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Protection: MSP RMM tools integrate with antivirus and anti-malware solutions, providing real-time protection against known and emerging threats.
- Firewall Management: MSP RMM tools can configure and manage firewalls on client devices, restricting access to unauthorized networks and applications.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: MSP RMM tools can monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activity, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data Loss Prevention: MSP RMM tools can prevent sensitive data from leaving the network, ensuring that confidential information remains secure.
Reporting
Reporting capabilities provide MSPs with valuable insights into the health and performance of their clients’ IT infrastructure. MSP RMM tools generate detailed reports that can be used to identify trends, track performance metrics, and make informed decisions.
- System Performance Reports: MSP RMM tools generate reports on system performance, including CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network activity. This allows MSPs to identify potential bottlenecks and resource constraints.
- Security Reports: MSP RMM tools provide reports on security events, including malware detections, intrusion attempts, and data loss incidents. This helps MSPs assess the security posture of their clients’ systems and identify areas for improvement.
- Patch Management Reports: MSP RMM tools generate reports on patch deployments, tracking the status of updates and identifying systems that require attention.
- Customizable Reports: MSP RMM tools allow MSPs to create custom reports tailored to their specific needs, providing insights into specific aspects of their clients’ IT infrastructure.
Integration with Other Tools
In today’s dynamic IT landscape, MSPs need a comprehensive approach to manage their clients’ technology infrastructure. Seamless integration between MSP RMM tools and other IT management solutions is crucial for streamlining workflows, reducing redundancy, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Successful integration enables MSPs to create a unified IT management environment, eliminating data silos and facilitating a holistic view of their clients’ IT operations. This unified approach improves visibility, simplifies troubleshooting, and empowers MSPs to proactively address potential issues before they impact end-users.
MSP RMM tools are essential for managing and monitoring client systems remotely, ensuring smooth operations and proactive maintenance. For efficient file management within these tools, consider integrating Far Manager , a powerful file manager with a user-friendly interface. Far Manager’s robust features can streamline tasks like file transfers, backups, and script execution, enhancing the overall efficiency of your MSP RMM operations.
Integration with PSA Tools
Integrating MSP RMM tools with Professional Services Automation (PSA) platforms, such as ConnectWise Manage, Autotask, or Kaseya, is essential for streamlining service delivery and billing processes. This integration allows MSPs to:
- Automatically create tickets in the PSA system when RMM alerts are triggered, ensuring timely issue resolution.
- Track time spent on tasks performed through the RMM tool, improving accuracy and efficiency in billing.
- Centralize client information and service contracts within the PSA platform, providing a comprehensive view of customer relationships.
Integration with Ticketing Systems
Integrating MSP RMM tools with ticketing systems, like Zendesk or Freshdesk, allows for efficient communication and collaboration between technicians and clients. This integration facilitates:
- Automatic ticket creation in the ticketing system when RMM alerts are triggered, ensuring timely communication with clients.
- The ability to track ticket status and progress within the RMM tool, providing visibility into issue resolution.
- Centralized communication channels, simplifying communication and reducing the risk of missed information.
Integration with Cloud Platforms
Integrating MSP RMM tools with cloud platforms, such as Microsoft Azure or AWS, allows for efficient management of cloud-based resources. This integration enables MSPs to:
- Monitor cloud infrastructure performance and resource utilization, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Automate cloud provisioning and configuration tasks, reducing manual effort and potential errors.
- Implement security policies and controls for cloud resources, enhancing data protection and compliance.
Security and Compliance
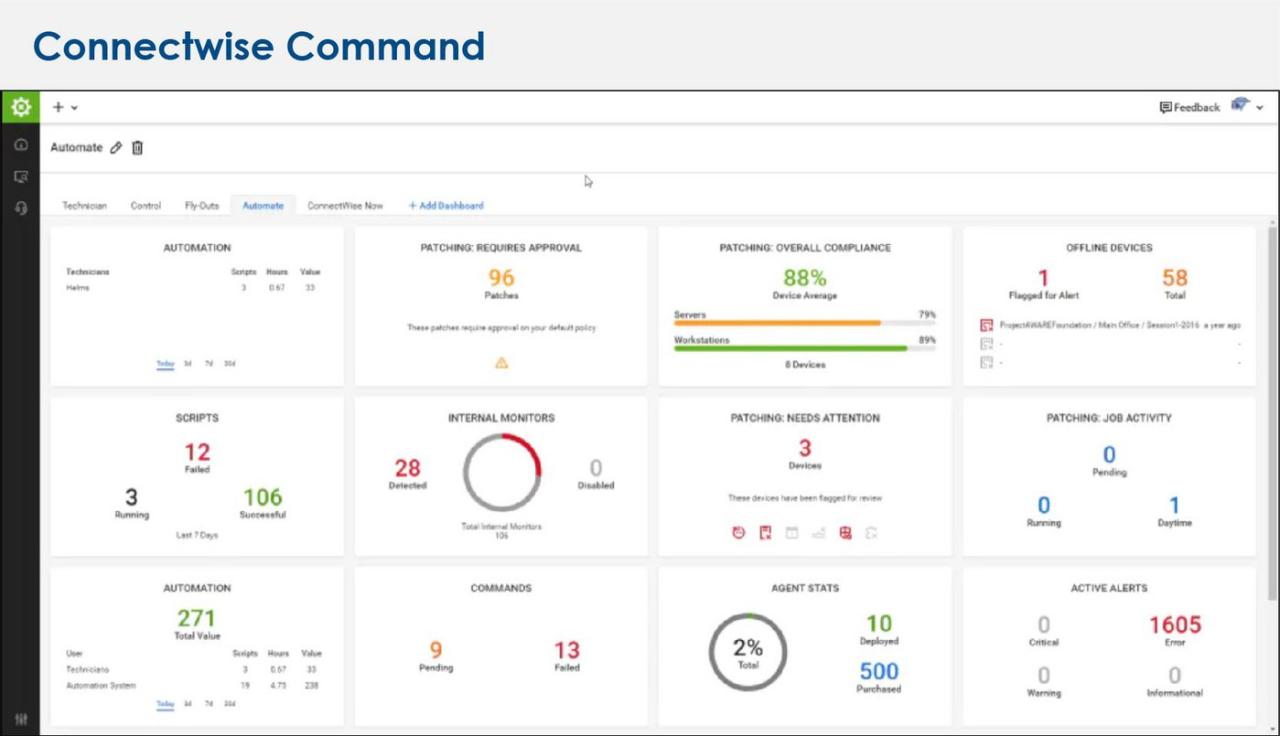
MSP RMM tools play a crucial role in maintaining data security and compliance for managed service providers (MSPs) and their clients. By automating security tasks, enforcing policies, and monitoring systems, RMM solutions help MSPs protect sensitive information, mitigate risks, and ensure adherence to industry regulations.
Vulnerability Management
RMM tools enable proactive vulnerability management by identifying and patching security flaws in software and operating systems. They scan systems for vulnerabilities, prioritize remediation efforts based on risk levels, and automate patch deployment. This approach helps MSPs stay ahead of potential threats and reduce the risk of exploitation.
Security Policy Enforcement
RMM solutions facilitate the implementation and enforcement of security policies across managed endpoints. MSPs can configure policies to restrict access to sensitive data, control user permissions, and enforce password complexity requirements. These policies help maintain a consistent level of security across all managed devices.
Compliance Standards Support
MSP RMM tools support compliance with various industry standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. They offer features like data encryption, access control, and audit logging, which are essential for meeting regulatory requirements.
“By automating security tasks and providing comprehensive reporting capabilities, RMM tools help MSPs demonstrate compliance and maintain a strong security posture.”
Security Features
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Protection: RMM tools often integrate with leading antivirus and anti-malware solutions, providing real-time protection against threats.
- Endpoint Security: They offer features like firewall management, intrusion detection, and data loss prevention to secure endpoints from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Network Security: RMM tools can monitor network traffic, identify suspicious activity, and enforce network access policies.
- Data Encryption: They support data encryption at rest and in transit, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Security Auditing: RMM tools provide comprehensive audit logs, enabling MSPs to track security events, identify potential breaches, and comply with regulatory requirements.
- User Authentication and Access Control: They facilitate secure user authentication and granular access control, limiting access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Patching: RMM tools automate vulnerability scanning, prioritize patching efforts based on risk levels, and deploy patches across managed endpoints.
Best Practices for MSP RMM Implementation
Successfully implementing an MSP RMM tool requires careful planning and execution. By following best practices, MSPs can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of using an RMM tool.
Understanding Your Business Needs
Defining your business needs is crucial before choosing and implementing an RMM tool. This involves identifying the specific challenges you face and the desired outcomes from using an RMM solution. For example, consider the types of devices you manage, the size of your client base, and the level of automation you require.
- Identify your pain points: Determine the specific issues you are facing, such as slow response times, frequent security breaches, or difficulty managing remote devices. This will help you choose an RMM tool that addresses your unique needs.
- Define your goals: Clearly articulate what you hope to achieve by implementing an RMM tool. For example, you may aim to improve client satisfaction, reduce operational costs, or enhance security posture. This will guide your decision-making process and help you measure success.
- Assess your resources: Consider your budget, available staff, and technical expertise. This will help you select an RMM tool that is affordable, manageable, and compatible with your existing infrastructure.
Choosing the Right RMM Tool
Selecting the right RMM tool is essential for successful implementation. Consider the features, pricing, and compatibility of different RMM solutions to find the best fit for your business.
- Features: Look for an RMM tool that offers the features you need, such as remote access, patch management, endpoint security, and reporting. Consider the specific requirements of your client base and the types of devices you manage.
- Pricing: Compare the pricing models of different RMM tools and choose one that fits your budget. Consider factors such as the number of devices you manage, the level of support you require, and the features included in each pricing plan.
- Compatibility: Ensure the RMM tool is compatible with your existing infrastructure, including your operating systems, software, and network configurations. Check for compatibility with other tools you use, such as ticketing systems or monitoring platforms.
Planning and Implementing the RMM Solution
After choosing an RMM tool, you need to plan and implement it effectively. This involves setting up the RMM platform, configuring policies, and training your staff.
- Set up the RMM platform: Install the RMM agent on all client devices and configure the platform according to your business needs. This includes setting up user accounts, defining policies, and configuring reporting options.
- Configure policies: Define policies for patch management, endpoint security, and other tasks. Ensure these policies are tailored to your specific requirements and align with your security best practices.
- Train your staff: Provide your staff with adequate training on using the RMM tool. This includes understanding its features, configuring policies, and troubleshooting issues. Proper training ensures your team can effectively manage the RMM solution and provide excellent client support.
Managing User Roles and Permissions
Establishing a robust user management system is crucial for security and efficiency. This involves defining different user roles and assigning appropriate permissions to each role.
- Define user roles: Create different user roles based on responsibilities, such as administrators, technicians, and clients. This ensures that each user has access to the appropriate information and functionalities.
- Assign permissions: Assign specific permissions to each user role. For example, administrators may have full access to the RMM platform, while technicians may have limited access to specific client devices. This helps maintain security and control over sensitive information.
- Regularly review permissions: Periodically review user roles and permissions to ensure they remain appropriate and aligned with your security policies. This helps prevent unauthorized access and maintain a secure environment.
Monitoring and Optimization
Continuously monitor the RMM solution’s performance and optimize its settings to ensure optimal efficiency and effectiveness. This includes analyzing reports, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments.
- Analyze reports: Regularly review reports generated by the RMM tool to identify trends, performance issues, and potential security threats. This data provides valuable insights into the overall health of your managed devices.
- Identify areas for improvement: Use the reports to identify areas where the RMM solution can be optimized. For example, you may need to adjust policies, streamline workflows, or enhance security measures.
- Make necessary adjustments: Implement changes based on your analysis and monitoring. This ensures the RMM solution remains effective and meets your evolving business needs.
Case Studies and Success Stories
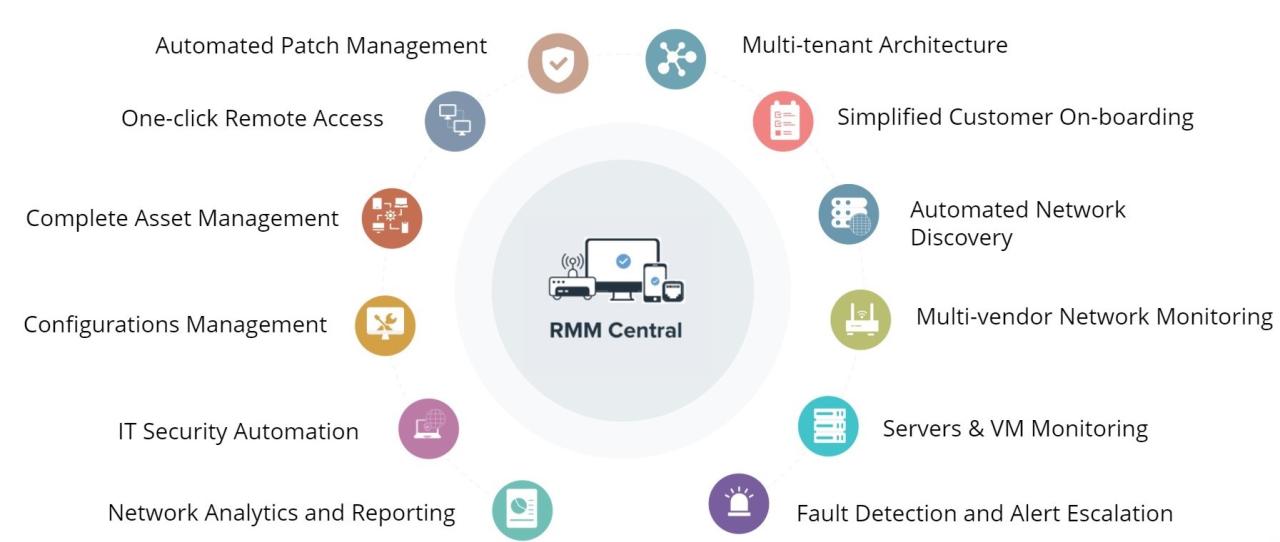
Real-world examples showcase the tangible benefits MSPs experience when implementing RMM tools. These case studies illustrate how RMM solutions contribute to improved business outcomes and enhanced client satisfaction. By examining these success stories, MSPs can gain valuable insights into the practical applications and the value proposition of RMM tools.
Impact on Business Outcomes
RMM tools have demonstrably improved key business outcomes for MSPs. Here are some real-world examples:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: A mid-sized MSP implemented an RMM tool and experienced a 25% reduction in time spent on routine tasks, such as patching and software updates. This freed up valuable resources for more strategic initiatives and client engagement.
- Reduced Costs: By automating tasks and proactively identifying potential issues, an RMM solution helped an MSP reduce their support costs by 15%. This resulted in improved profitability and a stronger competitive advantage.
- Improved Client Satisfaction: A smaller MSP reported a significant increase in client satisfaction after deploying an RMM tool. Proactive monitoring and rapid issue resolution led to a 10% decrease in service tickets and a 5% improvement in client retention rates.
Impact on Client Satisfaction
RMM tools have a direct impact on client satisfaction by enhancing the overall service experience. Here are some examples:
- Faster Response Times: An RMM solution enabled an MSP to proactively monitor client systems and detect issues before they impacted users. This resulted in a 50% reduction in service ticket resolution times, leading to improved client satisfaction.
- Improved Security Posture: By automating security updates and implementing proactive threat detection, an RMM tool helped an MSP improve their clients’ security posture. This resulted in fewer security incidents and increased client confidence in their IT infrastructure.
- Enhanced Communication and Transparency: An RMM solution allowed an MSP to provide clients with real-time updates on the status of their systems and service requests. This increased transparency and communication, leading to a more positive client experience.
Value Proposition of MSP RMM
These case studies highlight the value proposition of MSP RMM tools:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By automating tasks and streamlining workflows, RMM tools free up MSP resources, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities, such as client relationship management and strategic planning.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance: RMM solutions provide robust security features, including vulnerability scanning, endpoint protection, and compliance monitoring, ensuring that client systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations.
- Increased Profitability: RMM tools contribute to improved profitability by reducing support costs, increasing efficiency, and enabling MSPs to manage more clients with fewer resources.
- Enhanced Client Satisfaction: By providing proactive monitoring, rapid issue resolution, and improved security, RMM tools lead to a more positive client experience, fostering stronger client relationships and loyalty.
MSP RMM Resources: Msp Rmm Tools
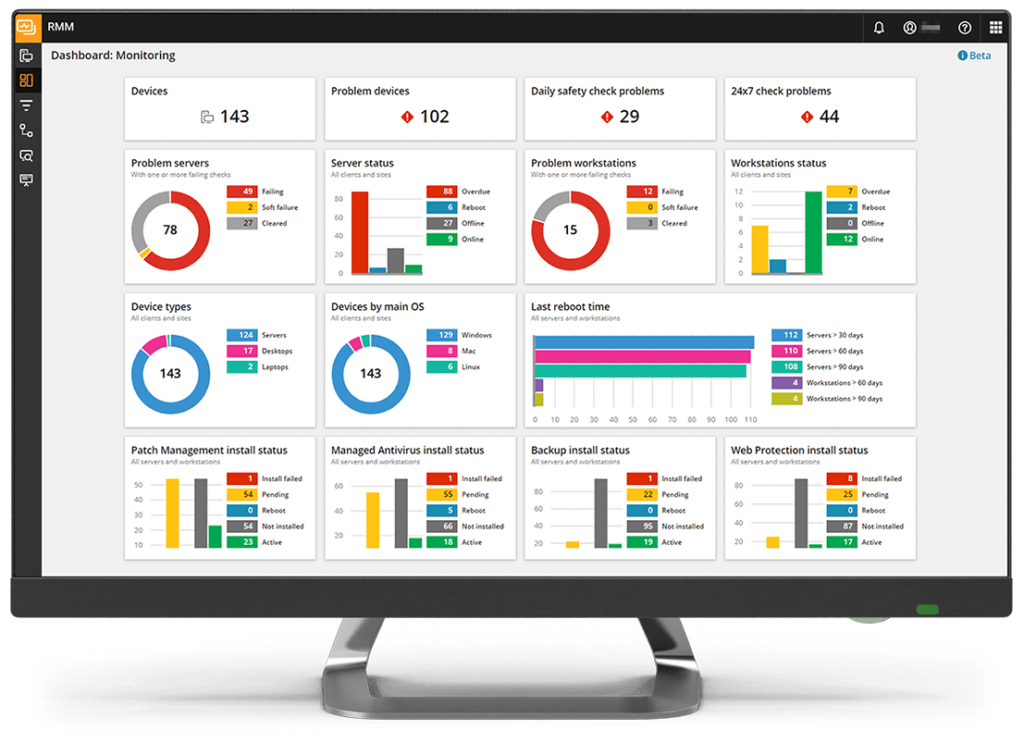
The journey to mastering MSP RMM tools doesn’t end with the initial setup. Continuous learning and exploration of available resources are crucial for staying ahead of the curve and maximizing the benefits of these tools. This section Artikels valuable resources for MSPs looking to deepen their understanding and enhance their RMM expertise.
Industry Websites and Forums
These platforms serve as valuable hubs for knowledge sharing, discussions, and staying updated on the latest trends in the MSP RMM landscape.
- MSPmentor: A leading online community for MSPs, providing news, articles, and discussions on RMM tools and other relevant topics.
- The IT Business Edge: A reputable resource offering insightful articles and expert opinions on RMM solutions, best practices, and industry developments.
- Reddit’s r/MSP: A vibrant online community where MSPs can engage in discussions, seek advice, and share experiences related to RMM tools and other MSP-related topics.
Vendor Documentation
Comprehensive documentation provided by RMM tool vendors is an invaluable resource for understanding the functionalities, configurations, and troubleshooting aspects of their respective solutions.
- Knowledge Bases: Most vendors offer extensive knowledge bases containing articles, tutorials, and FAQs to address common issues and provide detailed explanations of features.
- User Manuals: Detailed user manuals provide comprehensive guides on all aspects of the RMM tool, including installation, configuration, and advanced usage.
- Online Forums: Many vendors maintain dedicated online forums where users can connect with each other, seek support, and share best practices.
Training Programs and Certifications
Formal training programs and certifications can enhance an MSP’s knowledge and credibility in the field of RMM.
- Vendor-Specific Training: Many RMM vendors offer training programs, workshops, and certifications to help MSPs become proficient in using their tools effectively.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Organizations like CompTIA and Microsoft offer certifications related to IT infrastructure management, which can be beneficial for MSPs working with RMM tools.
Epilogue
In conclusion, MSP RMM tools are an indispensable asset for any managed service provider seeking to optimize operations, enhance client satisfaction, and navigate the complexities of modern IT management. By embracing the power of these tools, MSPs can unlock a world of possibilities, delivering exceptional service, improving security, and driving greater efficiency across their client base. The future of MSP RMM is bright, with continued innovation and advancements promising even greater levels of automation, intelligence, and security in the years to come.