MSP Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) is a game-changer for managed service providers (MSPs) and their clients. It empowers MSPs to proactively monitor, manage, and secure their clients’ IT infrastructure remotely, enhancing efficiency and security while reducing downtime and costs.
Table of Contents
RMM solutions provide a centralized platform for managing multiple client environments, offering real-time insights into system health, performance, and security. This allows MSPs to identify and address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring seamless operations and optimal performance for their clients.
What is MSP Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM)?
MSP Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) is a powerful suite of tools that enables Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to remotely monitor, manage, and support their clients’ IT infrastructure. RMM solutions offer a comprehensive approach to IT management, allowing MSPs to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact end-users.
Core Functionality of RMM Solutions
RMM solutions provide a range of functionalities to streamline IT management for MSPs.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM tools allow MSPs to securely connect to and control client devices remotely, enabling them to troubleshoot problems, install software, and perform other tasks without physically being on-site.
- System Monitoring: RMM solutions continuously monitor critical system parameters, such as CPU usage, disk space, and network connectivity. This allows MSPs to identify potential issues early and prevent downtime.
- Patch Management: RMM tools automate the process of applying security patches and updates to client systems, ensuring that all devices are protected from vulnerabilities.
- Backup and Recovery: RMM solutions often include backup and recovery features, allowing MSPs to protect client data from disasters and ensure rapid data restoration.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM tools provide comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling MSPs to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make informed decisions about IT infrastructure management.
Benefits of Implementing RMM for MSPs and Their Clients
Implementing RMM offers numerous benefits for both MSPs and their clients.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: RMM tools automate many repetitive IT tasks, freeing up MSP technicians to focus on more complex issues. This results in improved efficiency and productivity for both the MSP and their clients.
- Improved Security: RMM solutions help MSPs proactively identify and address security threats, reducing the risk of data breaches and other cyberattacks. This is particularly important in today’s increasingly complex threat landscape.
- Reduced Downtime: By monitoring systems and proactively resolving issues, RMM tools help prevent downtime and ensure that client businesses can operate smoothly. This is crucial for businesses that rely on their IT infrastructure to function.
- Enhanced Client Satisfaction: By providing faster and more responsive IT support, MSPs can improve client satisfaction and build stronger relationships. This is essential for retaining clients and growing the MSP business.
- Cost Savings: RMM tools can help MSPs reduce costs by automating tasks, minimizing downtime, and improving efficiency. This can lead to lower IT expenses for both the MSP and their clients.
Examples of Typical Tasks Automated by RMM Tools
RMM tools automate a wide range of tasks, including:
- Software Deployment and Updates: RMM tools can automatically deploy software and updates to client devices, ensuring that all systems are running the latest versions.
- Security Patch Management: RMM solutions automate the process of applying security patches to client systems, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus and Malware Protection: RMM tools can manage antivirus and malware protection for client devices, ensuring that they are protected from threats.
- System Monitoring and Alerting: RMM solutions monitor critical system parameters and send alerts to MSP technicians when issues arise, allowing them to take corrective action promptly.
- Backup and Recovery: RMM tools automate the process of backing up client data and restoring it in the event of a disaster.
- Remote Desktop Support: RMM tools allow MSP technicians to remotely access and control client devices, providing quick and efficient support.
Types of RMM Solutions: Msp Remote Monitoring & Management
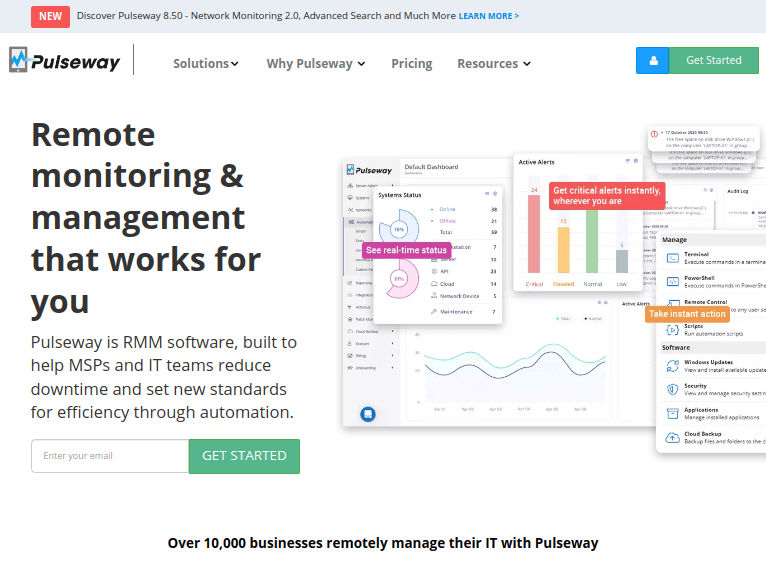
RMM solutions are available in different forms, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the distinctions between these types is crucial for choosing the right solution for your organization’s needs.
Types of RMM Solutions
The three main types of RMM solutions are cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid.
- Cloud-based RMM: These solutions are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. This eliminates the need for on-site hardware and software installations, simplifying setup and maintenance.
- On-premises RMM: On-premises solutions are installed and run directly on your organization’s servers. This provides greater control over data and security but requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
- Hybrid RMM: Hybrid solutions combine aspects of both cloud-based and on-premises RMM. They offer flexibility and control while leveraging the benefits of cloud technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different RMM Types, Msp remote monitoring & management
Each type of RMM solution has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
| RMM Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Cloud-based RMM |
|
| On-premises RMM |
|
| Hybrid RMM |
|
RMM Deployment & Implementation
Deploying and implementing an RMM solution is a crucial step for MSPs to gain control over their clients’ IT infrastructure. This process involves a series of steps and requires careful planning to ensure a seamless integration within an MSP’s existing infrastructure.
Deployment Steps
The deployment of an RMM solution involves a series of steps that should be carefully planned and executed. These steps include:
- Assessment: The first step is to assess the current IT infrastructure of the client. This involves understanding the client’s existing systems, applications, and network configuration. The assessment helps determine the scope of the RMM deployment and identify any potential challenges.
- Solution Selection: After the assessment, MSPs need to select an RMM solution that best suits the client’s needs. This includes considering factors like the size of the client’s environment, the types of devices to be managed, and the budget. MSPs can choose from a variety of RMM solutions, each with its own features and pricing models.
- Installation & Configuration: Once the solution is selected, the next step is to install and configure the RMM agent on each device within the client’s network. This involves deploying the agent, configuring its settings, and integrating it with the RMM platform.
- Testing & Optimization: After installation, it’s crucial to test the RMM solution to ensure it’s working correctly and meeting the client’s requirements. This involves running various tests, monitoring performance, and fine-tuning settings for optimal performance.
- Training & Support: Once the RMM solution is deployed, it’s essential to provide training to the client’s IT staff on how to use the platform. This ensures that the client can effectively utilize the RMM solution for managing their IT infrastructure. Ongoing support is also critical for addressing any issues or questions that may arise.
Best Practices for RMM Integration
Successful RMM integration within an MSP’s existing infrastructure requires adherence to best practices:
- Clear Communication: Maintaining clear and consistent communication with clients is crucial throughout the deployment process. This involves keeping clients informed about the progress, addressing any concerns, and providing regular updates.
- Automation: Leveraging automation tools can significantly streamline the RMM deployment process. Automation can automate tasks like agent deployment, configuration, and patch management, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
- Security: Security is paramount during RMM deployment. MSPs should ensure that the RMM solution is secure and compliant with industry standards. This involves implementing strong authentication mechanisms, encrypting data in transit and at rest, and regularly updating the RMM platform and agents.
- Scalability: The RMM solution should be scalable to accommodate the client’s future growth. This involves choosing a solution that can handle an increasing number of devices, users, and data without compromising performance.
- Monitoring & Reporting: Regular monitoring and reporting are essential to ensure the RMM solution is performing as expected. This involves tracking key metrics, generating reports, and identifying any potential issues or areas for improvement.
Potential Challenges During Deployment
Deployment of an RMM solution can present challenges:
- Compatibility Issues: One common challenge is compatibility issues between the RMM solution and the client’s existing IT infrastructure. This could involve issues with operating systems, applications, or network devices. Thorough testing and troubleshooting are essential to address such compatibility issues.
- Security Concerns: Clients may have concerns about security when deploying an RMM solution. MSPs should address these concerns by providing detailed information about the security measures implemented in the RMM solution and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- User Adoption: Another challenge is user adoption. Clients and their IT staff may be hesitant to use a new RMM solution. MSPs should provide comprehensive training and support to encourage user adoption and ensure the RMM solution is effectively utilized.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the RMM solution with other existing tools and systems can be complex. MSPs should carefully plan the integration process, ensure compatibility, and provide adequate training to ensure seamless integration.
- Cost Considerations: The cost of deploying and maintaining an RMM solution can be a significant factor for clients. MSPs should clearly communicate the pricing structure, provide value-based justification for the investment, and explore cost-effective options.
Solutions for Deployment Challenges
To overcome the challenges during RMM deployment, MSPs can adopt the following solutions:
- Pilot Deployment: A pilot deployment allows MSPs to test the RMM solution in a controlled environment before deploying it across the client’s entire network. This helps identify and address any potential issues early on.
- Phased Rollout: A phased rollout involves deploying the RMM solution in stages, starting with a small group of devices or users. This allows for gradual testing and feedback, reducing the risk of widespread disruptions.
- Third-Party Integration: MSPs can leverage third-party integrations to connect the RMM solution with other tools and systems. This can simplify integration and enhance functionality.
- Ongoing Support: Providing ongoing support and training to clients is crucial for ensuring successful RMM adoption. MSPs should offer proactive monitoring, troubleshooting, and regular updates to address any issues or questions.
- Clear Communication: Maintaining open and transparent communication with clients throughout the deployment process is essential. This involves providing regular updates, addressing concerns, and ensuring client buy-in.
Security & Compliance in RMM
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are powerful tools for managing IT infrastructure, but they also introduce new security and compliance considerations. It is crucial to ensure that the RMM solution itself is secure and that it is used in a way that complies with relevant regulations.
Security Features in RMM
Security features in RMM solutions are designed to protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, before granting access to the RMM platform. This makes it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access, even if they have stolen a password.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): RBAC ensures that users only have access to the data and functionalities they need to perform their jobs. This helps to prevent accidental or malicious data breaches.
- Data encryption: RMM solutions should encrypt data both in transit and at rest. This means that data is protected from unauthorized access even if the RMM platform is compromised.
- Security audits and logging: Regular security audits and detailed logging can help to identify potential security vulnerabilities and track user activity.
- Regular security updates: RMM solutions should be updated regularly to patch vulnerabilities and address security threats.
Compliance Considerations in RMM
RMM solutions must comply with various regulations, including:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation requires organizations to protect the personal data of individuals in the European Union. RMM solutions must be GDPR-compliant to ensure that they handle personal data in accordance with the regulation.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): This regulation applies to organizations that handle protected health information (PHI). RMM solutions used in healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA to ensure that PHI is protected from unauthorized access.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): This standard applies to organizations that handle credit card data. RMM solutions used by organizations that handle credit card data must comply with PCI DSS to ensure that this data is protected.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): This act requires publicly traded companies to implement internal controls over financial reporting. RMM solutions can help organizations meet SOX compliance by providing visibility into IT systems and processes.
RMM for Enhanced Security and Compliance
RMM solutions can significantly enhance security posture and compliance efforts by:
- Centralized management and control: RMM provides a single platform for managing security settings, policies, and updates across multiple devices. This helps to ensure that security measures are consistently applied and that all devices are compliant with regulations.
- Proactive threat detection and response: RMM solutions can monitor systems for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential threats. This allows for faster incident response and helps to minimize the impact of security breaches.
- Automated patch management: RMM solutions can automate the process of patching vulnerabilities and updating software. This helps to reduce the risk of exploits and ensures that devices are protected from the latest threats.
- Compliance reporting and auditing: RMM solutions can generate reports that demonstrate compliance with various regulations. This helps to simplify compliance audits and provides evidence that security measures are being implemented effectively.
RMM & Remote Support
RMM solutions play a crucial role in enhancing remote support capabilities for MSPs, enabling them to effectively troubleshoot issues and deliver proactive maintenance services. RMM tools empower MSPs to remotely access and manage client systems, facilitating seamless and efficient support, regardless of location.
Remote Support & Troubleshooting
RMM platforms provide a comprehensive set of tools that streamline remote support and troubleshooting processes. These tools include:
- Remote Desktop Access: RMM enables MSPs to establish secure remote connections to client devices, allowing them to view desktops, access files, and perform tasks as if they were physically present. This facilitates immediate problem diagnosis and resolution.
- Remote Command Execution: MSPs can execute commands remotely on client devices, such as restarting services, installing software updates, or running scripts. This empowers them to resolve issues quickly and efficiently without requiring onsite visits.
- File Transfer: RMM tools enable secure file transfer between the MSP and client devices. This allows for easy transfer of software, configuration files, or diagnostic logs, facilitating efficient troubleshooting.
- Real-Time Monitoring: RMM provides real-time monitoring of client systems, allowing MSPs to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify potential issues before they escalate, and proactively address problems.
- Automated Task Scheduling: RMM platforms enable the scheduling of automated tasks, such as software updates, system backups, or security scans. This ensures that routine maintenance activities are performed regularly, reducing the risk of system failures and security breaches.
Proactive Support & Maintenance
RMM tools empower MSPs to provide proactive support and maintenance services, preventing issues before they impact clients.
- Automated Alerts & Notifications: RMM systems generate alerts and notifications when issues are detected, such as system errors, hardware failures, or security threats. This allows MSPs to address problems before they escalate, minimizing downtime and potential disruptions.
- Performance Optimization: RMM provides insights into system performance, enabling MSPs to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and improve overall system efficiency. This can help prevent performance issues and ensure smooth operation.
- Security Monitoring & Patching: RMM tools monitor security vulnerabilities and automatically deploy security patches, ensuring that client systems are protected against malware and other threats. This proactive approach reduces the risk of security breaches and data loss.
- Backup & Disaster Recovery: RMM platforms can automate backup processes, ensuring that client data is regularly backed up and protected against data loss. This facilitates rapid recovery in case of system failures or data breaches.
RMM in Remote Support Scenarios
RMM is invaluable in various remote support scenarios, including:
- Troubleshooting Software Issues: RMM allows MSPs to remotely access client systems and diagnose software issues, such as application crashes or performance problems. They can then resolve the issue remotely, minimizing downtime and disruption for the client.
- Addressing Hardware Failures: RMM can help identify hardware failures, such as failing hard drives or faulty network components. MSPs can then guide clients through troubleshooting steps or arrange for replacement parts, minimizing the impact of hardware issues.
- Implementing Security Updates: RMM enables MSPs to quickly and securely deploy security updates and patches to client systems, ensuring that they are protected against the latest threats. This proactive approach reduces the risk of security breaches and data loss.
- Managing Remote Workers: RMM is essential for managing remote workers, ensuring that their devices are secure, compliant, and functioning optimally. MSPs can remotely monitor and manage these devices, providing support and troubleshooting as needed.
Final Summary
In conclusion, MSP remote monitoring and management solutions are a valuable tool for MSPs looking to optimize their operations, enhance client satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge. By embracing RMM, MSPs can streamline their processes, improve security posture, and provide exceptional service to their clients. As technology continues to evolve, RMM will play an increasingly vital role in the future of managed IT services.
MSP remote monitoring and management can be a game-changer for businesses of all sizes, ensuring systems run smoothly and proactively preventing issues. One tool that can help with creative tasks is mypaint , a free and open-source digital painting program.
While mypaint focuses on artistic expression, MSP solutions offer the same level of control and efficiency but for your entire IT infrastructure.