Blender App is a powerful, open-source 3D creation suite that empowers users to design, animate, and render stunning visuals. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious beginner, Blender offers a comprehensive toolkit to bring your creative visions to life.
Table of Contents
From intricate 3D models to captivating animations, Blender provides the tools and flexibility to tackle a wide range of projects. Its intuitive interface, extensive community support, and vast library of tutorials make it an accessible platform for both beginners and experts.
Key Features and Capabilities
Blender is a free and open-source 3D creation suite. It offers a comprehensive set of tools for modeling, sculpting, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing, and motion tracking. Its vast capabilities and intuitive interface have made it popular among professionals and hobbyists alike.
3D Modeling
Blender provides a wide range of tools for creating 3D models. These tools allow users to create complex objects from simple shapes, edit existing models, and create detailed textures and materials.
- Mesh Modeling: This is the most common type of 3D modeling in Blender. It involves creating and manipulating polygons, which are the basic building blocks of 3D models. Blender provides a wide range of tools for creating, editing, and manipulating meshes, including tools for extruding, beveling, subdividing, and smoothing.
- Sculpting: Blender’s sculpting tools allow users to create organic shapes and details by manipulating a 3D mesh with brushes. This technique is often used for creating characters, creatures, and other organic objects.
- Curve Modeling: This technique uses curves to define the shape of an object. Blender provides a variety of tools for creating and manipulating curves, which can be used to create smooth and elegant shapes.
- Surface Modeling: This technique involves creating and manipulating surfaces, which are 2D objects that can be used to create complex 3D shapes. Blender’s surface modeling tools allow users to create NURBS surfaces, which are often used for creating smooth, curved objects.
Animation
Blender’s animation tools allow users to bring their 3D models to life. Users can create keyframes to define the movement of objects over time, and use a variety of tools to control the motion of their animations.
- Keyframing: This is the most basic form of animation in Blender. It involves setting keyframes at specific points in time to define the position, rotation, and scale of an object. Blender provides a variety of tools for creating and editing keyframes, including tools for setting keyframes on multiple objects simultaneously, creating smooth transitions between keyframes, and animating properties such as material settings and object visibility.
- Constraints: These are special tools that allow users to control the motion of objects in a more sophisticated way. Constraints can be used to limit the movement of an object, make an object follow a specific path, or make an object track another object’s motion.
- Inverse Kinematics (IK): This is a powerful technique that allows users to control the motion of a chain of objects by moving a single target object. IK is often used for animating characters, robots, and other objects with complex limbs.
- Motion Tracking: This technique allows users to track the movement of objects in a real-world video sequence and use that data to animate 3D objects in their scene. Motion tracking can be used to create realistic effects such as adding 3D objects to a real-world video or animating 3D characters to interact with real-world footage.
Rendering
Blender’s rendering engine allows users to create photorealistic images and animations of their 3D scenes. Blender offers a variety of rendering options, including ray tracing, path tracing, and cycles rendering.
- Cycles: Blender’s production-ready, physically based rendering engine that supports features like ray tracing, path tracing, and physically accurate materials. It is capable of producing high-quality, photorealistic images and animations.
- Eevee: A real-time rendering engine that is optimized for speed and interactivity. It is ideal for creating quick renders and previewing scenes in real time. While it doesn’t have the same level of realism as Cycles, Eevee is still capable of producing impressive results.
- Materials and Textures: Blender supports a wide range of materials and textures, allowing users to create realistic and visually appealing surfaces. These materials can be customized with properties such as color, reflectivity, transparency, and roughness. Users can create their own custom materials and textures or use pre-made materials from the Blender library.
- Lighting: Blender provides a variety of lighting tools, including point lights, directional lights, area lights, and spotlights. These lights can be used to illuminate scenes and create realistic shadows and reflections.
File Formats
Blender supports a wide range of file formats for importing and exporting data. This allows users to collaborate with other 3D software and use Blender as a central hub for their 3D projects.
- Import: Blender can import a wide variety of file formats, including 3DS, OBJ, FBX, DXF, STL, and more.
- Export: Blender can export its data in a variety of formats, including OBJ, FBX, 3DS, STL, and more.
User Interface and Workflow
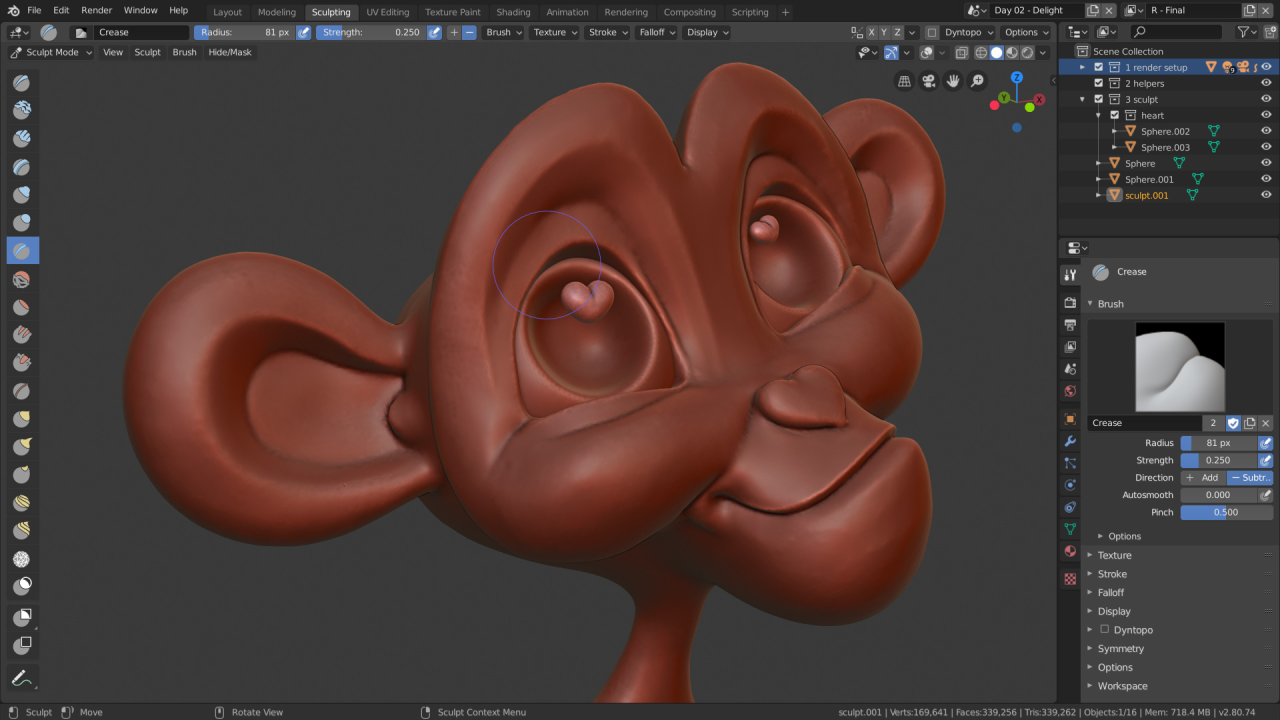
Blender’s interface, while initially appearing complex, is designed for intuitive and efficient 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. Its layout is organized around a central 3D viewport, surrounded by various tool panels and windows.
The interface provides a comprehensive set of tools and features, catering to both beginners and experienced users. It offers a flexible and customizable workspace, allowing users to arrange panels and windows to suit their workflow.
Navigating the Interface
The interface consists of several key components:
- 3D Viewport: This is the central area where you interact with and manipulate 3D objects. It provides various viewing modes, including perspective, orthographic, and camera views.
- Tool Panels: These panels, located on the sides and bottom of the interface, offer access to a wide range of tools and settings. They are organized into categories, such as modeling, sculpting, animation, and rendering.
- Artikelr: The Artikelr displays a hierarchical view of all objects, materials, and other elements in your scene, allowing you to easily select and manage them.
- Properties Panel: This panel, typically found on the right side of the interface, provides detailed settings and properties for selected objects, materials, and other elements.
- Header Bar: The header bar at the top of the interface provides access to file operations, rendering controls, and other general settings.
To navigate the interface effectively, you can use the following techniques:
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Blender utilizes a vast array of keyboard shortcuts to quickly access tools and commands. Learning and utilizing these shortcuts significantly enhances workflow efficiency.
- Mouse Interaction: The mouse is used for selecting objects, manipulating tools, and navigating the 3D viewport. Blender supports various mouse gestures for specific actions, such as panning, zooming, and rotating the view.
- Menu System: The menu bar at the top of the interface provides access to a comprehensive range of commands and settings. It is organized into categories, such as File, Edit, View, and Window.
Common Workflows
Blender offers various workflows for creating and editing 3D models, depending on the specific task and desired outcome. Some common workflows include:
- Modeling: This workflow involves creating and manipulating 3D objects using various modeling tools, such as extrusion, beveling, and subdivision.
- Mesh Modeling: This involves creating and manipulating polygonal meshes, which are composed of vertices, edges, and faces.
- Curve Modeling: This involves creating and manipulating 2D curves, which can be extruded or revolved to form 3D objects.
- Surface Modeling: This involves creating and manipulating smooth surfaces, such as NURBS surfaces.
- Sculpting: This workflow involves shaping and detailing 3D models using digital sculpting tools, providing a more organic and free-form approach to modeling.
- Dynamic Topology: This sculpting technique allows you to add and remove detail in real-time, adjusting the mesh resolution as needed.
- Retopology: This process involves creating a clean and optimized mesh from a sculpted model, improving its efficiency for animation and rendering.
- Animation: This workflow involves bringing 3D models to life by creating sequences of movement.
- Keyframing: This involves setting key poses at specific points in time, allowing you to control the object’s movement and rotation.
- Constraints: These tools allow you to define relationships and dependencies between objects, simplifying animation tasks.
- Motion Tracking: This technique allows you to track real-world footage and use it as a basis for animation.
- Rendering: This workflow involves creating final images or videos from your 3D scene.
- Cycles: This is Blender’s physically based renderer, providing realistic and high-quality results.
- Eevee: This is Blender’s real-time renderer, offering a faster and more interactive rendering experience.
- Materials and Textures: These elements define the appearance and surface properties of objects in your scene.
Learning Resources and Community
Blender is a powerful and versatile 3D creation suite that has a vibrant and supportive community. There are many resources available for learning Blender, from official documentation to online tutorials and communities. This section will discuss the various resources available to help users learn and master Blender.
Tutorials and Documentation
Blender offers a wealth of resources for learning the software, including official documentation, tutorials, and online communities. The Blender Foundation provides extensive documentation that covers all aspects of the software, from basic concepts to advanced techniques. The Blender Manual is a comprehensive guide that explains all the features and tools available in Blender. The Blender website also features a large collection of tutorials, covering a wide range of topics, including modeling, animation, rendering, and scripting. These tutorials are created by experienced Blender users and are designed for users of all skill levels.
Online Communities
Blender has a large and active community of users who are always willing to help each other. There are many online forums, support groups, and communities dedicated to Blender, where users can ask questions, share tips and tricks, and collaborate on projects. The Blender Artists forum is one of the most popular online communities for Blender users. It features a variety of forums for discussing different aspects of Blender, as well as a gallery where users can share their work. The Blender Stack Exchange is another valuable resource for Blender users, providing a platform for asking and answering technical questions.
Community Contributions
The Blender community is a key factor in the software’s success. Users contribute to the software’s development by creating add-ons, scripts, and other tools that enhance Blender’s functionality. These contributions are often shared freely with the community, making Blender even more powerful and versatile. The Blender community also contributes to the software’s documentation and tutorials, ensuring that there are resources available for users of all skill levels.
Blender App for Beginners
Blender is a powerful and versatile 3D creation suite that can be used for everything from modeling and animation to rendering and compositing. While Blender’s capabilities are vast, it can also seem daunting to newcomers. This guide provides a step-by-step introduction to Blender, equipping beginners with the essential tools and techniques to navigate the world of 3D creation.
Getting Started with Blender
Beginners can start with the default “Cube” object, which serves as a foundational element for learning Blender’s interface and tools. To access this, open Blender and press “Delete” to remove the default scene, then press “Shift + A” and select “Mesh” > “Cube.” This creates a cube in the center of the 3D viewport.
Essential Tools and Techniques for Beginners, Blender app
This section delves into the core tools and techniques crucial for beginners to understand and master.
Interface Overview
Blender’s interface is unique and may initially seem overwhelming. However, understanding its components is essential for navigating the software. The main areas of the Blender interface include:
- 3D Viewport: This is where the 3D scene is displayed and manipulated. It allows users to rotate, zoom, and pan the camera view to examine the scene from different angles.
- Toolbar: Located on the left side of the screen, the Toolbar contains tools for selecting, moving, rotating, and scaling objects.
- Properties Panel: Found on the right side of the screen, the Properties Panel displays detailed settings and options for selected objects or tools.
- Artikelr: This panel, usually located on the bottom right, provides a hierarchical view of all objects in the scene.
- Timeline: Located at the bottom of the screen, the Timeline allows users to control the animation process, setting keyframes and adjusting the playback speed.
Basic Modeling Techniques
Modeling forms the foundation of 3D creation. Here are some essential modeling techniques for beginners:
- Vertex, Edge, and Face Selection: These are the fundamental building blocks of any 3D object. Understanding how to select and manipulate them is crucial. To select vertices, edges, or faces, use the corresponding selection modes in the Toolbar.
- Extrude: This tool allows users to create new geometry by pushing out existing faces, edges, or vertices. Extrude can be used to add depth to objects or create complex shapes.
- Loop Cut: This technique allows users to add new edges and vertices along a specific path, creating more detailed geometry.
- Subdivision Surface: This modifier smooths out the edges of an object, creating a more rounded and organic appearance.
Navigation and Manipulation
Navigating and manipulating objects in Blender is key to creating 3D scenes.
- Orbit: This allows users to rotate the camera around the scene, enabling viewing from different angles. To orbit, use the middle mouse button or the “Alt” key with the left mouse button.
- Pan: This moves the camera horizontally or vertically within the scene. To pan, use the middle mouse button with the “Shift” key or the “Alt” key with the right mouse button.
- Zoom: This adjusts the camera’s distance from the scene, allowing users to zoom in for detail or zoom out for a broader perspective. To zoom, use the scroll wheel on the mouse or the “Alt” key with the scroll wheel.
- Selection: Select objects using the left mouse button. To select multiple objects, hold down the “Shift” key and click on each object. To select all objects in the scene, press “A.”
- Transform: This includes moving, rotating, and scaling objects. To move an object, press “G” and drag the mouse. To rotate an object, press “R” and drag the mouse. To scale an object, press “S” and drag the mouse.
Lighting and Materials
Lighting and materials play a crucial role in creating visually appealing 3D scenes.
- Adding Lights: Blender offers various types of lights, including point lights, spotlights, and area lights. To add a light, press “Shift + A” and select “Light” from the menu.
- Materials: Materials define the appearance of objects in a scene, including their color, texture, and reflectivity. To add a material, select an object and go to the “Material” tab in the Properties Panel. You can then create a new material and customize its properties.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Navigating Blender can present various challenges for beginners.
Learning Curve
Blender’s interface and workflow can seem complex, especially for those new to 3D software. However, it’s important to remember that the learning curve is gradual. Start with simple tutorials and gradually explore more advanced features as you gain confidence.
Troubleshooting
Blender’s error messages can be cryptic, making it difficult to troubleshoot issues.
“If you encounter an error, don’t panic. Try to identify the cause of the error by examining the error message and the context in which it occurred. Search online forums or documentation for similar issues and their solutions.”
Finding Resources
Blender’s vast community offers a wealth of resources for learning and troubleshooting.
- Official Documentation: Blender’s official documentation provides comprehensive information on all aspects of the software.
- Online Tutorials: Many online platforms offer free and paid tutorials on Blender. Some popular resources include Blender Guru, CG Cookie, and YouTube channels dedicated to Blender.
- Community Forums: Blender’s online forums are excellent places to ask questions and seek help from experienced users.
Blender App and Emerging Technologies
Blender is a powerful and versatile 3D creation suite, constantly evolving to embrace cutting-edge technologies. Its integration with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies is opening up new possibilities for creating immersive and interactive experiences.
Blender App and VR/AR Technologies
The integration of Blender with VR and AR technologies is transforming the way we create and interact with digital content. Blender’s tools allow users to design and develop VR and AR experiences, including virtual worlds, interactive simulations, and augmented reality applications.
- VR Development: Blender’s VR tools enable users to create virtual environments and objects that can be experienced in VR headsets. This includes modeling, texturing, animation, and rendering for VR applications.
- AR Development: Blender’s AR tools facilitate the creation of AR experiences that blend digital content with the real world. This involves designing 3D models, animations, and interactive elements that can be viewed through AR devices.
Blender App for Immersive Experiences
Blender’s capabilities in 3D modeling, animation, and rendering make it a powerful tool for creating immersive experiences. The software’s features allow users to design and develop interactive environments, realistic simulations, and engaging storytelling experiences.
- Interactive Environments: Blender can be used to create interactive virtual environments for gaming, training, and education. These environments can be populated with realistic characters, objects, and landscapes.
- Realistic Simulations: Blender’s simulation tools allow users to create realistic simulations of physical phenomena, such as fluid dynamics, particle systems, and cloth simulation. These simulations can be used for scientific research, engineering design, and entertainment.
- Engaging Storytelling: Blender’s animation and rendering capabilities can be used to create engaging stories and experiences. Users can create animated films, interactive narratives, and immersive virtual tours.
Blender App for 3D Printing and Advanced Applications
Blender’s versatility extends beyond visual effects and animation. It plays a crucial role in 3D printing, enabling users to design and create physical objects.
- 3D Printing: Blender allows users to create 3D models that can be printed using 3D printers. This enables the creation of prototypes, custom designs, and functional objects.
- Other Advanced Applications: Blender’s capabilities are also employed in fields like architecture, engineering, and product design. The software can be used to create architectural visualizations, product prototypes, and engineering simulations.
Case Studies of Blender App Projects
Blender has been used to create a wide range of impressive projects, showcasing its versatility and power. From stunning visuals for movies and video games to intricate models for architecture and product design, Blender has become an essential tool for professionals and hobbyists alike.
Examples of Successful Projects
The following table highlights a few notable projects created using Blender:
| Project Name | Description | Industry | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Buck Bunny | An open-source, animated short film that was created entirely using Blender. | Animation and Film | Showcased the capabilities of Blender for creating high-quality animation and helped to popularize the software. |
| Sintel | Another open-source, animated short film that demonstrated Blender’s ability to create realistic and visually stunning effects. | Animation and Film | Further solidified Blender’s reputation as a powerful tool for creating high-quality animation. |
| Tears of Steel | A short film that showcased Blender’s capabilities for creating complex and realistic CGI effects, including fluid simulations and motion capture. | Animation and Film | Helped to push the boundaries of what was possible with Blender and inspired other artists and filmmakers. |
| The Open Movie Project | A collaborative project that involved a large community of Blender users working together to create a full-length feature film. | Animation and Film | Demonstrated the power of open-source collaboration and the potential for Blender to be used for large-scale projects. |
Last Point

With its continuous development and a thriving community, Blender App is poised to remain a leading force in the 3D creation landscape. Whether you’re aiming to create breathtaking visuals for film and animation, design innovative products, or explore the world of virtual reality, Blender provides the tools and resources to unlock your creative potential.
Blender is a powerful open-source 3D creation suite, offering a wide range of tools for modeling, animation, and rendering. If you’re looking for a similar open-source option for document creation, you might want to check out project libre , which provides a comprehensive suite of office applications.
While Blender focuses on 3D creation, project libre empowers users to create and collaborate on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.

