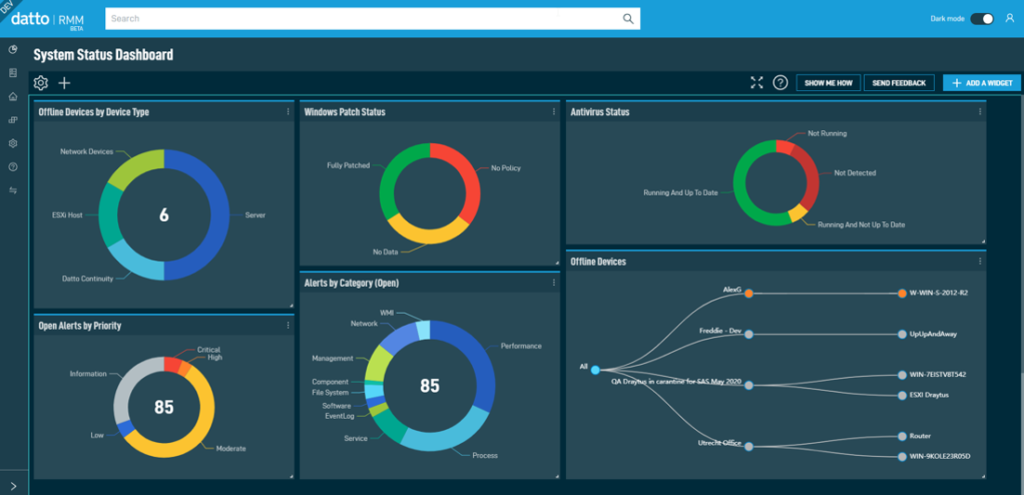
RMM tools, or Remote Monitoring and Management tools, are the unsung heroes of modern IT. These powerful platforms empower businesses to manage their technology infrastructure remotely, ensuring smooth operations and minimizing downtime.
Table of Contents
From patching vulnerabilities to automating routine tasks, RMM tools offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance efficiency, security, and compliance. By centralizing IT management, RMM solutions provide a single pane of glass for monitoring endpoints, deploying software updates, and addressing security threats proactively.
What are RMM Tools?
RMM tools, or Remote Monitoring and Management tools, are software solutions designed to simplify and streamline IT management tasks for businesses of all sizes. They provide a centralized platform for monitoring and managing computer systems, servers, networks, and other IT infrastructure remotely.
RMM tools empower IT professionals to proactively manage their IT environment, identify potential issues before they become critical, and resolve problems efficiently. They are essential for businesses looking to enhance IT security, improve system performance, and reduce operational costs.
Benefits of Using RMM Tools
RMM tools offer a wide range of benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved IT Security: RMM tools provide real-time monitoring of network activity, endpoint security, and user behavior, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of security threats.
- Enhanced System Performance: RMM tools help optimize system performance by monitoring resource utilization, identifying bottlenecks, and automatically applying updates and patches.
- Reduced IT Costs: RMM tools automate routine tasks, reduce the need for on-site visits, and minimize downtime, leading to significant cost savings.
- Increased Productivity: RMM tools free up IT professionals from manual tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives and improve overall productivity.
- Improved User Experience: RMM tools ensure smooth operation of IT systems, minimize disruptions, and provide prompt support to end-users.
Real-World Scenarios
Here are some real-world examples of how RMM tools demonstrate their value:
- Proactive Security Monitoring: An RMM tool detects suspicious activity on a company server, triggering an alert. The IT team investigates and discovers a malware infection. They quickly quarantine the infected server, preventing further damage and data breaches.
- Automated Patch Management: An RMM tool automatically deploys security patches to all company workstations, ensuring all systems are protected from known vulnerabilities. This eliminates the risk of manual updates and reduces the likelihood of security breaches.
- Remote Troubleshooting: An employee reports a slow computer. The IT team uses the RMM tool to remotely access the employee’s workstation, diagnose the problem, and resolve it without requiring an on-site visit.
Key Features of RMM Tools
RMM tools are packed with features designed to streamline IT management and bolster security. These features work in tandem to provide a comprehensive solution for managing your IT infrastructure effectively. Let’s delve into some of the most crucial RMM features.
Remote Access
Remote access allows IT professionals to connect to and manage devices remotely, regardless of their physical location. This eliminates the need for on-site visits, saving time and resources.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Access | Enables IT professionals to connect to and manage devices remotely, providing secure access to endpoints from anywhere. |
|
|
Patch Management
Patch management automates the process of updating software and operating systems on all devices, ensuring they have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patch Management | Automates the process of updating software and operating systems on all devices, ensuring they have the latest security patches and bug fixes. |
|
|
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security solutions protect individual devices from malware, viruses, and other threats. These tools provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, and remediation capabilities.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Security | Protects individual devices from malware, viruses, and other threats by providing real-time monitoring, threat detection, and remediation capabilities. |
|
|
Asset Management
Asset management provides a centralized inventory of all hardware and software assets within an organization, allowing for efficient tracking, monitoring, and management.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Management | Provides a centralized inventory of all hardware and software assets within an organization, allowing for efficient tracking, monitoring, and management. |
|
|
Types of RMM Tools
RMM tools are designed to cater to different needs and scales of businesses. Understanding the various types of RMM tools helps you choose the best fit for your organization.
RMM Tools Based on Target Audience
The target audience significantly influences the features and functionalities offered by RMM tools.
- Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs): RMM tools for SMBs are typically user-friendly and affordable. They focus on basic functionalities like remote access, patch management, and endpoint security. Examples include Atera, NinjaRMM, and ConnectWise Automate.
- Enterprises: Enterprise-grade RMM tools provide advanced features, scalability, and integration capabilities. They are designed to manage complex IT environments and often include features like compliance management, automation, and reporting. Examples include Datto RMM, Kaseya, and SolarWinds N-central.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise RMM Solutions
The deployment model of an RMM tool is another crucial factor to consider.
- Cloud-Based RMM: Cloud-based RMM solutions are hosted on a third-party server and accessible through a web browser. They offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced infrastructure costs. Examples include Datto RMM, Kaseya, and NinjaRMM.
- On-Premise RMM: On-premise RMM solutions are installed and managed within an organization’s own data center. They provide more control over data security and compliance but require significant upfront investment in hardware and IT resources. Examples include SolarWinds N-central, ConnectWise Automate, and LabTech.
Specialized RMM Tools for Specific Industries
Certain industries have unique IT security and compliance requirements. Specialized RMM tools cater to these specific needs.
- Healthcare: Healthcare RMM tools comply with HIPAA regulations and provide features for managing patient data, electronic health records (EHRs), and medical devices.
- Finance: Financial institutions require RMM tools that meet PCI DSS compliance standards and offer features for managing sensitive financial data, payment processing, and network security.
- Education: Education RMM tools are designed to manage student devices, network security, and data privacy, adhering to FERPA regulations.
Choosing the Right RMM Tool
Selecting the ideal RMM tool for your organization requires a comprehensive evaluation process. It’s not just about finding a tool with a lot of features; it’s about finding the one that best fits your specific needs and budget.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an RMM Tool
When choosing an RMM tool, it’s important to consider several factors. These factors will help you narrow down your options and select the best tool for your organization.
- Your budget: RMM tools can range in price from a few dollars per month to hundreds of dollars per month. It’s important to consider your budget and choose a tool that offers the features you need without breaking the bank.
- The size of your organization: If you have a small organization, you may not need all the features of a large-scale RMM tool. Conversely, if you have a large organization, you’ll need a tool that can handle the demands of your environment.
- The types of devices you need to manage: Some RMM tools are better suited for managing Windows devices, while others are better for managing Macs or mobile devices. Choose a tool that supports the types of devices you need to manage.
- The level of technical expertise of your IT team: Some RMM tools are more user-friendly than others. If your IT team is not very technical, you’ll want to choose a tool that is easy to use and learn.
- The level of support you need: Some RMM tools offer 24/7 support, while others offer limited support. Choose a tool that offers the level of support you need.
- The features you need: RMM tools offer a wide range of features, including remote access, patch management, software deployment, and endpoint security. Choose a tool that offers the features you need.
Features and Functionalities to Prioritize
It’s important to have a checklist of features and functionalities to prioritize during the evaluation process. This will help you compare different RMM tools and make an informed decision.
- Remote access: The ability to remotely access and control devices is essential for any RMM tool. This allows you to troubleshoot problems, install software, and manage devices from a central location.
- Patch management: Patch management is critical for keeping your devices secure. An RMM tool should allow you to automatically deploy patches to your devices, keeping them up-to-date with the latest security updates.
- Software deployment: Software deployment is another important feature of an RMM tool. This allows you to deploy software to your devices quickly and easily, without having to manually install it on each device.
- Endpoint security: Endpoint security is essential for protecting your devices from malware and other threats. An RMM tool should offer features such as antivirus protection, anti-malware protection, and firewall management.
- Reporting and analytics: Reporting and analytics features allow you to track the health and performance of your devices. This data can be used to identify potential problems, improve security, and optimize performance.
- Integration with other tools: The ability to integrate with other tools, such as ticketing systems, is important for streamlining your IT operations. Look for an RMM tool that integrates with the tools you already use.
Comparison of Popular RMM Tools
Here is a comparison of some popular RMM tools based on pricing, features, and user reviews.
| Tool | Pricing | Features | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atera | $79/month for 5 devices | Remote access, patch management, software deployment, endpoint security, reporting and analytics | 4.5/5 stars on G2 |
| ConnectWise Automate | $129/month for 10 devices | Remote access, patch management, software deployment, endpoint security, reporting and analytics, IT documentation, scripting | 4.2/5 stars on G2 |
| NinjaOne | $99/month for 10 devices | Remote access, patch management, software deployment, endpoint security, reporting and analytics, IT documentation, scripting | 4.4/5 stars on G2 |
| Datto RMM | $199/month for 25 devices | Remote access, patch management, software deployment, endpoint security, reporting and analytics, IT documentation, scripting, backup and disaster recovery | 4.3/5 stars on G2 |
| SolarWinds MSP | $149/month for 10 devices | Remote access, patch management, software deployment, endpoint security, reporting and analytics, IT documentation, scripting, backup and disaster recovery | 4.1/5 stars on G2 |
“Choosing the right RMM tool is an investment in the security and efficiency of your IT infrastructure. Take the time to carefully evaluate your needs and select a tool that will meet your specific requirements.”
Implementing and Managing RMM Tools
Successfully deploying and managing an RMM solution requires a strategic approach that encompasses careful planning, efficient implementation, and ongoing maintenance. This section delves into the essential steps involved in deploying an RMM solution and highlights the importance of continuous monitoring and maintenance. Additionally, we’ll discuss best practices for integrating RMM tools seamlessly with your existing IT infrastructure.
Deploying an RMM Solution
The process of deploying an RMM solution involves a series of steps that ensure a smooth and successful transition. These steps are crucial for establishing a robust and efficient remote management infrastructure.
- Choose an RMM tool: The initial step is selecting an RMM tool that aligns with your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the size of your organization, the complexity of your IT environment, and your budget.
- Plan the deployment: Before deploying the RMM tool, create a comprehensive deployment plan that Artikels the scope of the deployment, the target devices, and the timeline for implementation.
- Install the RMM agent: The RMM agent is a software component that needs to be installed on each device you want to manage remotely. Ensure you have the necessary permissions and access to install the agent on all target devices.
- Configure the RMM tool: After installation, configure the RMM tool to meet your specific requirements. This includes setting up policies, defining alerts, and configuring reporting options.
- Test and monitor: Once the RMM tool is configured, thoroughly test its functionality to ensure it’s working as expected. Continuous monitoring is essential to identify and address any issues promptly.
Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Maintaining the effectiveness and security of your RMM solution requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance. This involves regular tasks that ensure the tool remains updated, secure, and operating optimally.
- Regular updates: RMM vendors frequently release updates to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and introduce new features. Regularly update your RMM tool to ensure you’re benefiting from the latest enhancements and security patches.
- Security checks: Regularly audit the security settings of your RMM tool and ensure that access controls and user permissions are properly configured to prevent unauthorized access.
- Performance monitoring: Monitor the performance of the RMM tool and the devices it manages. Identify any performance bottlenecks or issues that may require attention.
- Backups and disaster recovery: Implement a robust backup and disaster recovery plan for your RMM tool and its associated data. This ensures that you can recover from data loss or system failures.
Integrating RMM Tools with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating an RMM tool with your existing IT infrastructure is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness and ensuring seamless operations. This involves establishing connections and configurations that allow the RMM tool to interact with other systems and applications.
- Active Directory integration: Integrating your RMM tool with Active Directory simplifies user management and allows for centralized control over device access and permissions.
- Network monitoring tools: Integrating your RMM tool with network monitoring tools provides a comprehensive view of your network infrastructure, enabling you to identify and resolve network-related issues proactively.
- Ticketing systems: Integrating your RMM tool with ticketing systems streamlines issue resolution by automatically creating tickets when alerts are triggered.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools: Integrating your RMM tool with SIEM tools provides a centralized platform for collecting and analyzing security events, enhancing threat detection and response capabilities.
RMM Tools and Security
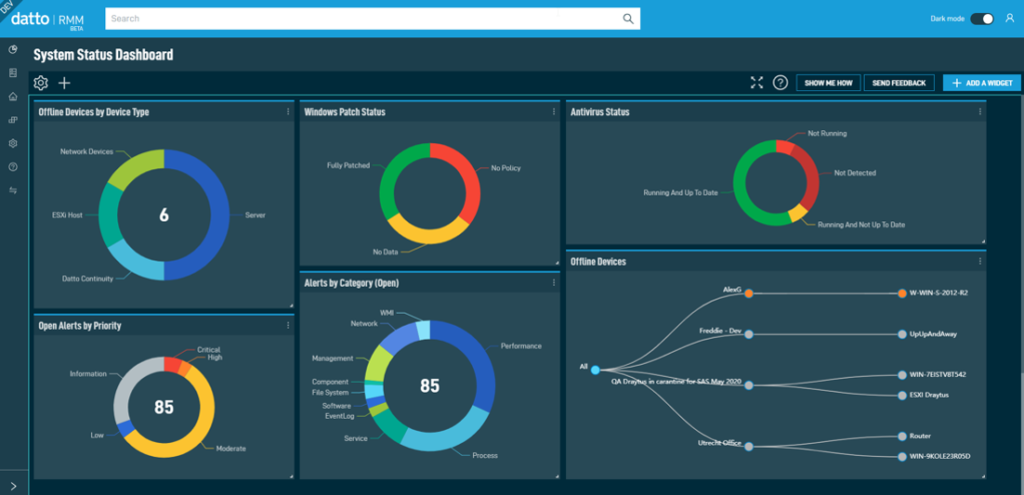
RMM tools play a crucial role in enhancing endpoint security by providing a centralized platform for managing and securing devices across an organization. These tools offer a comprehensive approach to endpoint security, encompassing vulnerability management, patch management, threat detection, and incident response.
RMM Tools and Endpoint Security Enhancement
RMM tools contribute significantly to endpoint security by automating tasks, streamlining processes, and providing real-time visibility into device activity. They empower organizations to proactively address security vulnerabilities, prevent attacks, and respond effectively to security incidents.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM tools automate the process of installing security patches, ensuring that systems are updated with the latest security fixes. This eliminates the risk of manual errors and delays, significantly reducing the window of vulnerability for attacks.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Remediation: RMM tools can automatically scan devices for known vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for remediation. This proactive approach helps organizations identify and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Real-time Monitoring and Alerting: RMM tools provide real-time monitoring of endpoint activity, detecting suspicious behavior and alerting administrators to potential threats. This allows organizations to respond quickly to security incidents, minimizing the impact of attacks.
- Endpoint Security Policy Enforcement: RMM tools enable organizations to enforce consistent security policies across all endpoints, ensuring that devices meet security standards and best practices. This includes policies related to password complexity, firewall configuration, and software restrictions.
RMM Tools and Security Threat Detection and Response
RMM tools equip organizations with the capabilities to detect and respond to security threats effectively. By leveraging real-time monitoring, threat intelligence, and automated response mechanisms, these tools enhance the organization’s security posture.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: RMM tools can integrate with threat intelligence feeds, enabling them to identify and block known malicious actors and activities. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Anomaly Detection and Behavioral Analysis: RMM tools can analyze endpoint activity to identify anomalies and deviations from normal behavior. This can help detect suspicious activity, such as unauthorized software installations or unusual network connections.
- Automated Incident Response: RMM tools can automate incident response actions, such as isolating infected devices, quarantining malicious files, and restoring compromised systems. This ensures a rapid and effective response to security incidents, minimizing the impact on business operations.
RMM Features for Enhanced Security Posture
Several RMM features contribute directly to strengthening an organization’s security posture. These features provide a comprehensive approach to security management, enabling organizations to effectively address vulnerabilities, prevent attacks, and respond to security incidents.
- Endpoint Security Software Integration: RMM tools can integrate with endpoint security software, such as antivirus, anti-malware, and intrusion detection systems, providing a unified platform for managing and monitoring security solutions.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM tools provide secure remote access and control capabilities, allowing administrators to troubleshoot issues, perform security updates, and respond to incidents remotely. This eliminates the need for physical access to devices, improving efficiency and security.
- Data Backup and Recovery: RMM tools can facilitate regular data backups and disaster recovery plans, ensuring that critical data is protected from security breaches and other unforeseen events. This safeguards business continuity and minimizes downtime.
RMM Tools and IT Automation
RMM tools play a crucial role in streamlining IT operations by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up valuable time for IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. They provide a centralized platform for managing and automating various IT processes, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Examples of Automated Processes
Automated processes using RMM tools can significantly simplify IT management and reduce the burden on IT teams. Here are some examples:
- Patch Management: RMM tools can automatically scan devices for missing patches, download and install updates, and ensure systems are protected against vulnerabilities.
- Software Deployment: Deploying software updates and applications to multiple devices can be automated, ensuring consistent and efficient distribution.
- Remote Monitoring and Management: RMM tools enable IT teams to remotely monitor and manage devices, including system performance, resource utilization, and security threats, from a central location.
- Backup and Recovery: Automating backup schedules and ensuring data recovery processes are in place can minimize downtime and data loss in the event of system failures.
- Endpoint Security: RMM tools can automatically implement security policies, scan for malware, and provide real-time threat detection and response.
- Asset Management: RMM tools can track hardware and software inventory, manage licenses, and provide insights into asset utilization.
- Ticket Management: Integrating RMM tools with ticketing systems can streamline issue resolution, allowing IT teams to quickly respond to user requests and resolve problems.
Benefits of Automation for IT Teams
Automation offers numerous benefits for IT teams, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automating repetitive tasks frees up IT professionals to focus on more complex and strategic initiatives, improving overall productivity.
- Reduced Errors: Automation eliminates manual errors, ensuring consistency and accuracy in IT processes.
- Improved Security: Automating security tasks like patch management and malware detection enhances system security and reduces vulnerability risks.
- Enhanced Scalability: RMM tools can easily scale to accommodate growing IT environments, providing consistent management and automation capabilities across multiple devices.
- Cost Savings: Automating tasks can reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency, resulting in significant cost savings for organizations.
RMM Tools and Compliance
RMM tools can be instrumental in helping businesses achieve and maintain compliance with various industry regulations. By automating tasks, monitoring systems, and providing comprehensive reporting, RMM solutions streamline compliance efforts, reduce risks, and ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory requirements.
Industry Regulations and RMM Tools
RMM tools can help businesses comply with a wide range of industry regulations, including:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): This law governs the protection of sensitive patient health information. RMM tools can help organizations comply with HIPAA by providing secure access controls, data encryption, and audit trails.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): This standard mandates security measures for organizations that process credit card payments. RMM tools can assist in meeting PCI DSS requirements by managing vulnerability assessments, enforcing strong passwords, and implementing network segmentation.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This regulation governs the processing of personal data of individuals within the European Union. RMM tools can help organizations comply with GDPR by providing data encryption, access control mechanisms, and data breach notification features.
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): This law requires publicly traded companies to implement internal controls over financial reporting. RMM tools can assist in SOX compliance by automating system and network monitoring, generating audit trails, and providing detailed reporting capabilities.
- GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act): This law protects the privacy of non-public personal financial information. RMM tools can help organizations comply with GLBA by providing data encryption, access control mechanisms, and secure data storage solutions.
How RMM Tools Assist in Compliance
RMM tools contribute to compliance in several ways:
- Automated Patch Management: RMM tools automate the process of applying security patches and updates, ensuring systems are protected against known vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Remediation: Regular vulnerability scans identify potential weaknesses in systems and networks, allowing for timely remediation and reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Security Configuration Management: RMM tools enforce security policies and configurations across devices, ensuring consistent security posture and reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Access Control and User Management: RMM solutions provide granular access control mechanisms, limiting access to sensitive data and resources based on user roles and permissions.
- Auditing and Reporting: RMM tools generate detailed audit trails and reports, documenting system activities and providing evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements.
Compliance-Related Features of RMM Solutions
Many RMM solutions offer specific features designed to support compliance:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit helps protect it from unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of authentication before accessing systems.
- Security Policy Enforcement: RMM tools can enforce security policies across devices, ensuring consistent security configurations.
- Compliance Reporting: RMM solutions generate reports that document compliance activities and provide evidence of adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Incident Response and Forensics: RMM tools can assist in incident response by providing information about system events and facilitating forensic investigations.
The Future of RMM Tools
The landscape of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing IT environments, and the growing demand for streamlined IT operations. This evolution promises to bring about significant changes in how businesses manage their IT infrastructure, impacting everything from security and compliance to automation and cost optimization.
Emerging Trends in the RMM Market
The RMM market is experiencing several emerging trends that are shaping the future of the technology. These trends are driven by a combination of factors, including the increasing complexity of IT environments, the growing importance of cybersecurity, and the need for greater automation and efficiency.
- Cloud-Based RMM Solutions: The adoption of cloud-based RMM solutions is accelerating, offering advantages such as scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based platforms allow businesses to manage their IT infrastructure from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for on-premises servers and software.
- Integration with Other IT Tools: RMM tools are increasingly integrating with other IT tools, such as ticketing systems, security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, and network monitoring tools. This integration creates a unified platform for managing all aspects of IT operations, providing a holistic view of the IT environment.
- Focus on Security and Compliance: Security and compliance are becoming increasingly important for businesses of all sizes. RMM tools are evolving to incorporate advanced security features, such as vulnerability scanning, endpoint protection, and data loss prevention, to help businesses meet regulatory requirements and protect their data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being integrated into RMM tools to automate tasks, improve security, and provide predictive insights. For example, AI-powered RMM tools can analyze system logs and identify potential threats before they escalate into security incidents.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming the way RMM tools operate, bringing about a new era of automation, intelligence, and proactive management. These technologies are being used to:
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks such as patch management, software updates, and system backups, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improve Security Posture: AI-powered RMM tools can analyze system logs and identify suspicious activity, detecting threats that might otherwise go unnoticed. They can also prioritize vulnerabilities and recommend remediation steps, enhancing the overall security posture of the IT environment.
- Provide Predictive Insights: By analyzing historical data, AI and ML can predict potential problems before they occur, allowing IT teams to proactively address issues and prevent downtime. For example, an AI-powered RMM tool could predict when a server is likely to fail based on its performance metrics, allowing IT professionals to take preventative measures.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: AI and ML can analyze usage patterns and identify areas where resources can be optimized, reducing costs and improving efficiency. For example, an AI-powered RMM tool could identify underutilized servers and recommend consolidating them to reduce energy consumption and hardware costs.
Predictions about the Future Direction of RMM Technology
The future of RMM technology is bright, with several exciting developments on the horizon. Here are some predictions about the future direction of RMM tools:
- Increased Focus on User Experience: RMM tools will become more user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and dashboards that provide clear insights into the health and performance of the IT environment. This will make RMM tools more accessible to non-technical users, empowering them to manage their own devices and applications.
- Greater Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT): As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, RMM tools will need to adapt to manage these devices effectively. This will involve incorporating new features for managing and securing IoT devices, ensuring their compatibility with the overall IT infrastructure.
- The Rise of “RaaS” (RMM as a Service): The “RaaS” model will become increasingly popular, allowing businesses to access RMM services on a subscription basis. This will provide businesses with a flexible and cost-effective way to manage their IT infrastructure, without the need for upfront investments in hardware or software.
- More Personalized and Adaptive RMM Solutions: RMM tools will become more personalized and adaptive, tailoring their functionality to the specific needs of individual businesses. This will involve using AI and ML to learn from user behavior and preferences, providing a more customized and efficient experience.
Closure
In today’s interconnected world, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, RMM tools are no longer a luxury but a necessity. By embracing these powerful solutions, businesses can gain peace of mind knowing their IT infrastructure is secure, optimized, and ready to support their evolving needs. The future of IT management is undoubtedly automated, and RMM tools are at the forefront of this exciting evolution.
RMM tools are essential for managing IT infrastructure efficiently. One crucial aspect of any IT business is billing, and billing petpooja offers a specialized solution for managing pet-related businesses. By seamlessly integrating billing processes, RMM tools can help businesses streamline operations and improve overall financial management.